| DSP Blockset |
 |
Index
- <1> <2> <3> <4> <5> <6> <7> <8> <9> <10> <11> <12> <13> <14>
- f (linear frequency). See frequencies
- fnyq (Nyquist frequency). See frequencies
- Fs (sample frequency or rate)
- See sample periods
- M (frame size). See frame sizes and matrices
- Mi (input frame size). See frame sizes
- Mo (output frame size). See frame sizes
- N (number of channels)
- See sample vectors and matrices
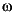 (digital frequency). See frequencies
(digital frequency). See frequencies
 (angular frequency). See frequencies
(angular frequency). See frequencies
 p (passband edge frequency)
p (passband edge frequency)
- See edge frequencies
 p1 (lower passband edge frequency)
p1 (lower passband edge frequency)
- See edge frequencies
 p2 (upper passband edge frequency)
p2 (upper passband edge frequency)
- See edge frequencies
 s (stopband edge frequency)
s (stopband edge frequency)
- See edge frequencies
 s1 (lower stopband edge frequency)
s1 (lower stopband edge frequency)
- See edge frequencies
 s2 (upper stopband edge frequency)
s2 (upper stopband edge frequency)
- See edge frequencies
- Rp (passband ripple). See passband ripple
- Rs (stopband attenuation)
- See stopband attenuation
- T (signal period). See periods
- Tf (frame period). See frame periods
- Tfi (input frame period). See frame periods
- Tfo (output frame period). See frame periods
- Ts (sample period). See sample periods <1> <2>
- Tsi (input sample period). See sample periods
- Tso (output sample period). See sample periods
- ../filterdesign/filterdesign_product_page.html
- 0s
- inserting <1> <2> <3>
- outputting
- Counter block
- Discrete Impulse block
- Integer Delay block
- N-Sample Enable block
- Signal From Workspace block <1> <2>
- padding with <1> <2>
- 1-D vectors
- 1s, outputting
- 2-norm
- acquiring data, blocks for
- adaptive filter designs
- blocks for
- FIR
- Kalman
- LMS
- RLS
- adaptive filters
- addition, cumulative
- algebraic loop errors
- algorithmic delay
- adjustable
- and initial conditions
- basic
- excess
- relation to latency
- zero
- Analog Filter Design block <1> <2> <3>
- analog filter designs <1> <2> <3>
- See also filter designs, continuous-time
- analytic signal
- Analytic Signal block
- angular frequency
- defined
- See also periods
- arrays
- exporting matrix data to
- importing
- attenuation, stopband
- audio
- exporting <1> <2> <3>
- importing <1> <2>
- autocorrelation
- and Levinson-Durbin recursion
- of a real vector
- sequence
- Autocorrelation block
- Autocorrelation LPC block
- autocorrelation method
- auto-promoting rates
- autoregressive models
- using Burg AR Estimator block
- using Burg Method block
- using the Covariance AR Estimator block
- using the Covariance Method block
- using the Modified Covariance AR Estimator block
- using the Modified Covariance Method block
- using the Yule-Walker AR Estimator block
- using the Yule-Walker Method block
- Backward Substitution block
- band configurations
- See filter band configurations
- bandpass filter designs
- analog, available parameters
- using Analog Filter Design block
- bandstop filter designs
- analog, available parameters
- using Analog Filter Design block
- Bartlett windows
- basic operations
- batch processing
- binary clock signals
- bins, histogram
- bit-reversed order
- Blackman windows
- block diagrams, creating
- blocks
- connecting
- multirate
- parameters for
- single-rate
- Buffer block <1> <2> <3>
- initial state of
- Buffer overlap parameter
- negative values for
- buffering <1> <2> <3>
- and rate conversion
- blocks for
- causing unintentional rate conversions
- example
- FIFO (first input, first output) register
- internally
- LIFO (last input, first output) register
- overlapping <1> <2>
- to create a frame-based signal
- with alteration of the signal <1> <2>
- with Delay Line block
- with preservation of the signal
- with Queue block
- with Stack block
- with Triggered Delay Line block
- Burg AR Estimator block
- Burg Method block
butter
- Butterworth filter designs
- analog
- band configurations for
- using Analog Filter Design block
- C code, generating
- channels
- in a frame-matrix
- of a sample-based signal
cheby1
cheby2
- Chebyshev type I filter designs
- analog
- band configurations for
- using Analog Filter Design block
- Chebyshev type II filter designs
- analog
- band configurations for
- using Analog Filter Design block
- Chebyshev windows <1> <2>
- Check Signal Attributes block
- Chirp block
- Cholesky Factorization block
- Cholesky Inverse block
- Cholesky Solver block
- clocks
- binary
- multiphase
- code generation
- generic real-time (GRT)
- minimizing size of
- using Real Time Workshop (RTW)
- code generation in the DSP Blockset
- color coding sample periods
- complex analytic signal
- Complex Cepstrum block
- Complex Exponential block
- complex exponentials <1> <2>
- computational delay
- concatenating
- to create multichannel signals <1> <2>
- Constant Diagonal Matrix block
- Constant Ramp block
- constants
- generating
- invariant (non-tunable)
- matrix <1> <2>
- precomputing
- ramp
- continuous-time signals
- continuous-time source blocks
- control signals
- for Triggered Shift Register block
- for Triggered Signal From Workspace block
- for Triggered Signal To Workspace block
- controller canonical forms
- conventions
- technical
- time and frequency
- Convert 1-D to 2-D block
- Convert 2-D to 1-D block
- converting
- frame rates. See rate conversion
- sample rates. See rate conversion
- convolution
- of two real vectors
- Convolution block
- correlation
- of two real vectors
- Correlation block
- correlation matrices
- Counter block
- Covariance AR Estimator block
- Covariance Method block
- Create Diagonal Matrix block
- creating signals
- Cumulative Product block
- Cumulative Sum block
- data type support
- Simulink custom data type
- data types
- labeling signals with
- dB Conversion block
- dB Gain block
- dB, converting to
- dBm, converting to
- DC component of an analytic signal
- DCT block
- DCTs
- computing
- decimation
- process of
- using FIR Decimation block
- using FIR Rate Conversion block
- default settings, Simulink
- delay
- algorithmic
- computational
- fractional <1> <2>
- generating <1> <2> <3>
- integer
- rebuffering <1> <2>
- relation to latency
- types of
- Delay Line block <1> <2> <3>
- demos
- running
- Demos library
- Detrend block
- diagonal matrix constants
- Difference block
- difference, between elements in a vector
- Digital Filter block
- Digital Filter Design block
- digital frequency
- defined
- See also periods
- discrete cosine transforms. See DCTs
- Discrete Impulse block
- discrete sample time, defined
- discrete wavelet transform
- discrete-time blocks
- nonsource
- source
- discrete-time signals
- characteristics
- defined
- terminology <1> <2>
- See also signals
- discretizing a continuous-time signal
- Display block
- display span
- in Vector Scope Block
- displaying
- blocks for
- frame-based data
- matrices as images
doc
- documentation
- Signal Processing Toolbox
- Downsample block <1> <2> <3>
- downsampling <1> <2> <3>
- See also rate conversion
- DSP Blockset
- documentation
- features
- getting started with
- installation
- organization
- overview
- required products
- DSP Constant block
dsp_links
dsplib <1> <2>
dspstartup M-file <1> <2>
- editing
- DWT block
- Dyadic Analysis Filter Bank block <1> <2>
- Dyadic Synthesis Filter Bank block <1> <2>
- Edge Detector block
- edge frequencies
- of analog filters
- edge frequencies, of analog filters
ellip
- elliptic filter designs
- analog
- band configurations for
- using Analog Filter Design block
- errors
- algebraic loop
- discrete-time source block
- due to continuous-time input to a discrete-time block
- due to insufficient audio buffer size
- sample-rate mismatch
- estimation
- nonparametric <1> <2>
- parametric
- using Burg AR Estimator block
- using Burg Method block
- using Covariance AR Estimator block
- using Covariance Method block
- using Modified Covariance AR Estimator block
- using Modified Covariance Method block
- using Yule-Walker AR Estimator block
- using Yule-Walker Method block
- Event-Count Comparator block
- events, triggering
- for N-Sample Enable block <1> <2>
- for Sample and Hold block
- for Stack block <1> <2>
- for Triggered Shift Register block
- for Triggered Signal From Workspace block
- for Triggered Signal To Workspace block
- exponentials, complex <1> <2>
- exporting
- blocks for <1> <2>
- sample-based signals
- using Triggered Signal To Workspace block
- exporting signals
- Extract Diagonal block
- Extract Triangular Matrix block
- f (linear frequency)
- defined
- See also frequencies
- fast Fourier transform (FFT)
- FDATool
- in the DSP Blockset
- features of DSP Blockset
- FFT block
- FFT length parameter
- FFTs
- and overlap-add filtering
- and overlap-save filtering
- computing
- filter band configurations
- bandpass
- using Analog Filter Design block
- bandstop
- using Analog Filter Design block
- highpass
- using Analog Filter Design block
- lowpass
- using Analog Filter Design block
- filter designs
- analog. See filter designs, continuous-time
- Butterworth
- using Analog Filter Design block
- using
butter
- Chebyshev type I
- band configurations for
- using Analog Filter Design block
- using
cheby1
- Chebyshev type II
- band configurations for
- using Analog Filter Design block
- using
cheby2
- continuous-time <1> <2>
- available parameters
- band configurations for
- edge frequency for
- passband ripple for
- stopband attenuation for
- Digital Filter block
- elliptic
- band configurations for
- using Analog Filter Design block
- using
ellip
- FIR
- using Levinson-Durbin block
- with prescribed autocorrelation sequence
- IIR
- continuous-time
- in the Digital Filter Design block
- Filter Realization Wizard
- filter realizations
- using Filter Realization Wizard
- filtering
- adaptive. See adaptive filter designs <1> <2>
- analog
- by overlap-add method
- by overlap-save method
- multirate
- filters
- designing, analyzing, and implementing
- example
- analyze, design, implement
- implement predesigned
- implementing predesigned
- multirate
- FIR
- interpolation using
- FIR Decimation block <1> <2>
- FIR filter designs
- using Levinson-Durbin block
- with prescribed autocorrelation sequence
- FIR Interpolation block <1> <2>
- FIR Rate Conversion block <1> <2>
- first-input, first-output (FIFO) registers
- fixed-step solvers <1> <2>
- Flip block
- fn (normalized frequency)
- defined
- See also frequencies
- fnyq (Nyquist frequency)
- defined
- See also frequencies
- Forward Substitution block
- frame
- defined
- See also frame-based signals
- frame periods
- altered by buffering
- altered by unbuffering
- constant <1> <2>
- converting. See rate conversion
- defined <1> <2>
- inspecting
- inspecting, using the Simulink Probe block
- multiple
- related to sample period and frame size <1> <2>
- frame rates
- auto-promoting
- See also frame periods
- frame sizes
- constant <1> <2>
- converting
- by direct rate conversion
- by rebuffering
- to maintain constant frame rate <1> <2>
- to maintain constant sample rate <1> <2>
- See also rate conversion
- defined <1> <2>
- related to sample period and frame period
- frame status
- converting
- defined
- Frame Status Conversion block
- frame-based processing
- and latency
- benefits
- frame-based signals
- benefits of
- changing frame size
- converting to sample-based signals <1> <2>
- creating
- creating from sample-based signals
- unbuffering
- frame-matrices
- format of
- frames
- changing size of
- unbuffering to scalars
- Framing parameter
- frequencies
- normalized
- normalized linear
- terminology
- See also periods <1> <2> <3>
- frequency distributions
- computing
- From Wave Device block
- From Wave File block
- Fs (sample frequency or rate)
- defined
- See also sample periods
- functions, utility
dsp_links
dsplib
dspstartup <1> <2>
rebuffer_delay
startup
startupsav
- gain, applying in dB
- generated code
- generic real-time (GRT)
- size of
- generating signals
- Hamming windows
- Hann windows
- Help Browser, accessing
- help, accessing
helpdesk
- highpass filter designs
- continuous-time
- using Analog Filter Design block
- Hilbert transformer filter designs
- Histogram block <1> <2>
- histograms, computing
- Hz (Hertz)
- defined
- See also sample periods
- IDCT block
- IDCTs
- computing
- identity matrices
- Identity Matrix block
- IFFT block
- IFFTs
- computing
- IIR filter designs
- continuous-time
- images, displaying matrices as
- importing
- arrays
- blocks for
- frame-based signals
- pages of an array
- sample-based matrices
- sample-based signals <1> <2> <3>
- sample-based vectors
- scalars
- signals <1> <2> <3>
- vectors
- indexing
- to deconstruct multichannel signals
inf parameter setting
- Inherit Complexity block
- inheriting sample periods
- initial conditions, with basic algorithmic delay
- Inline Parameters check box
- input frame periods
- defined
- See also frame periods
- input frame sizes. See frame sizes
- input periods. See also frame periods
- input sample periods. See sample periods
- installing the DSP Blockset
- Integer Delay block
- initial conditions for <1> <2>
- interpolating <1> <2>
- procedure
- Interpolation block
InvariantConstants parameter
- inverse discrete cosine transforms. See IDCTs
- Kaiser windows <1> <2>
- Kalman Adaptive Filter block
- last-input, first-output (LIFO) registers
- latency
- due to frame-based processing
- example
- predicting
- reducing
- relation to delay
- LDL Factorization block
- LDL Inverse block
- LDL Solver block
- least mean-square algorithm
- Least Squares Polynomial Fit block
- length of a vector
- defined
- See also frame sizes
- Levinson-Durbin block
- libraries
- Demos
- displaying link information
- Simulink <1> <2>
- Statistics
- Library Browser, using
- line widths
- displaying
- linear algebra
- linear prediction, using LPC block
- LMS Adaptive Filter block
- LMS algorithm
- loop-rolling
- lowpass filter designs
- continuous-time
- using Analog Filter Design block
- LPC to LSP/LSF Conversion block
- LSF/LSP to LPC Conversion block
- LU Factorization block
- LU Inverse block
- LU Solver block
- M (frame size). See frame sizes and matrices
- Magnitude FFT block
- magnitude response
- of Butterworth filters
- of Chebyshev type I filters
- of Chebyshev type II filters
- of elliptic filters
- magnitudes
- converting to dB
- MATLAB
- Demos window
- matrices
- 2-norm
- diagonal <1> <2>
- dimensions
- defined
- displaying
- as images
- extracting diagonal of
- extracting triangle from
- frame-based
- format of
- generated by buffering
- identity <1> <2>
- multiplying
- multiplying within
- normalizing
- number of channels in
- overwriting elements of
- permuting
- scaling
- selecting elements from
- summing
- support for
- Toeplitz
- transposing
- Matrix 1-Norm block
- Matrix Concatenation block
- Matrix Multiply block
- Matrix Product block
- Matrix Scaling block
- Matrix Square block
- Matrix Sum block
- in tutorial
- Matrix Viewer block <1> <2>
- maximum
- Maximum block
- mean
- computing
- Mean block <1> <2>
- Median block
- memory
- conserving
- M-files
dspstartup <1> <2>
- running simulations from
startup
startupsav
- Mi (input frame size). See frame sizes
- minimum
- Minimum block
- MMSE
- Mo (output frame size). See frame sizes
- models
- building
- defining
- multirate
- simulating
- modes, tasking
- Modified Covariance AR Estimator block
- Modified Covariance Method block
- mono inputs
- multichannel signals
- constructing <1> <2>
- deconstructing
- See also signals <1> <2>
- Multiphase Clock block
- multiplication, cumulative
- multiplying
- by dB gain
- matrices
- Multi-port Selector block
- multirate blocks
- multirate filtering <1> <2>
- multirate models <1> <2>
- multi-tasking mode
- multitasking mode
- N (number of channels)
- See sample vectors and matrices
- Normalization block
- normalized frequencies
- defined
- See also frequencies
- norms, 2-norm
- N-Sample Enable block
- N-Sample Switch block
- n-step forward linear predictors
- Nyquist frequency
- defined
- Nyquist rate
- defined
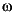 (digital frequency)
(digital frequency)
- defined
- See also frequencies
 (angular frequency)
(angular frequency)
- defined
- See also frequencies
 p (passband edge frequency)
p (passband edge frequency)
- See edge frequencies
 p1 (lower passband edge frequency)
p1 (lower passband edge frequency)
- See edge frequencies
 p2 (upper passband edge frequency)
p2 (upper passband edge frequency)
- See edge frequencies
 s (stopband edge frequency)
s (stopband edge frequency)
- See edge frequencies
 s1 (lower stopband edge frequency)
s1 (lower stopband edge frequency)
- See edge frequencies
 s2 (upper stopband edge frequency)
s2 (upper stopband edge frequency)
- See edge frequencies
- ones, outputting
- online help
- Out block, suppressing output
- Output check box
- output frame periods
- defined
- See also frame periods
- output frame sizes. See frame sizes
- output periods. See frame periods
- output sample periods. See sample periods
- Overlap-Add FFT Filter block <1> <2>
- overlap-add method
- overlapping buffers <1> <2>
- causing unintentional rate conversions
- Overlap-Save FFT Filter block <1> <2>
- overlap-save method
- overview of DSP Blockset
- Overwrite Values block
- Pad block
- pages of an array
- defined
- exporting
- pages of an array, importing
- parameters
- Buffer overlap, negative values for
- changing during simulation
- continuous-time filter
- definition of
InvariantConstants
- normalized frequency
RTWOptions
SaveOutput
SaveTime
- setting
- Simulink
Solver
StopTime
- tuning
- parametric estimation
- Partial Unbuffer block
- partial unbuffering
- passband ripple
- analog filter
- performance, improving <1> <2> <3>
- periodograms
- periods
- defined
- See sample periods and frame periods
- Permute Matrix block
- phase angles, unwrapping
- phase unwrap
- Polynomial Evaluation block
- Polynomial Stability Test block
- polyphase filter structures <1> <2> <3>
- ports, connecting
- power spectrum estimation
- using the Burg method <1> <2> <3>
- using the short-time, fast Fourier transform (ST-FFT)
- using the Yule-Walker AR method
- prediction, linear
- predictor algorithm
- Probe block
- example
- Pseudoinverse block
- QR Factorization block
- QR Solver block
- Quantizer block
- Queue block
- Quicksort algorithm
- radians
- ramp signal
- random signals
- Random Source block
- random-walk Kalman filter
- rate conversion <1> <2>
- blocks for
- by buffering
- by unbuffering
- direct <1> <2>
- overview
- to avoid rate-mismatch errors
- unintentional <1> <2>
- rate types
- block
- model
- rates
- auto-promoting
- See also sample periods and frame periods
- Real Cepstrum block
- Real-Time Workshop
- and loop-rolling
- generating generic real-time (GRT) code
- Real-Time Workshop panel
rebuffer_delay <1> <2>
- rebuffering <1> <2> <3>
- blocks for
- causing unintentional rate conversions
- delay <1> <2>
- computing
- procedure
- with alteration of the signal <1> <2>
- with preservation of the signal <1> <2>
- Reciprocal Condition block
- rectangular windows
- recursive least-squares (RLS) algorithm
- Remez exchange algorithm
- Repeat block <1> <2>
- resampling <1> <2> <3> <4> <5>
- by inserting zeros
- procedure
- ripple, passband
- RLS (recursive least-squares) algorithm
- RLS Adaptive Filter block
- RMS block <1> <2>
- RMS, computing
- root-mean-square. See RMS <1> <2>
- Rp (passband ripple)
- See passband ripple
- Rs (stopband attenuation)
- See stopband attenuation
- RTW. See Real-Time Workshop
RTWOptions parameter
- running operations
- Sample and Hold block
- sample frequency
- definition
- See also sample periods
- sample modes
- sample periods
- altered by buffering
- altered by unbuffering
- color coding
- continuous-time
- converting <1> <2>
- See also rate conversion
- defined <1> <2> <3> <4>
- discrete-time
- for Buffer block
- for frame-based signals
- for nonsource blocks
- for Rebuffer block
- inherited
- input, defined
- inspecting
- using color coding
- using the Simulink Probe block <1> <2>
- maintaining constant <1> <2>
- of source blocks
- output, defined
- related to frame period and frame size <1> <2>
- See also frame periods and sample times
- sample rates
- auto-promoting
- changing <1> <2>
- defined <1> <2>
- inherited
- overview
- See also sample periods
- Sample time colors option
- Sample time of original time series parameter
- Sample time parameter
- sample times
- color coding
- defined <1> <2> <3>
- shifting with sample-time offsets
- See also sample periods and frame periods
- sample-based signals <1> <2>
- converting to frame-based signals
- creating from frame-based signals
- importing <1> <2>
- samples
- adding <1> <2>
- defined
- deleting <1> <2>
- rearranging
- sampling
- See also sample periods and frame periods
SaveOutput parameter
SaveTime parameter
- scalars
- converting to vectors <1> <2>
- creating from vectors
- exporting
- importing <1> <2>
- Scope block
- scopes
- seconds
- selecting
- elements of a vector
- Selector block
- sequences
- defining a discrete-time signal
- settings, Simulink
- Shift Register block
- initial state of
- Short-Time FFT block
- short-time, fast Fourier transform (ST-FFT) method
- Signal dimensions
- Signal From Workspace block
- compared to Simulink To Workspace block
- Signal Processing Toolbox
- documentation
- Signal To Workspace block
- signals
- continuous-time
- control <1> <2> <3>
- discrete-time
- characteristics
- defined
- inspecting the sample period of
- terminology <1> <2>
- exporting
- frame-based
- benefits
- converting to sample-based <1> <2>
- multichannel
- frequency of, defined <1> <2>
- generating
- importing <1> <2>
- sample-based
- multichannel <1> <2>
- Nyquist frequency, defined
- Nyquist rate, defined
- period of, defined
- random
- sample-based <1> <2>
- converting to frame-based
- Simulation Parameters dialog box <1> <2> <3> <4>
- accessing
- simulations
- accelerating <1> <2> <3>
- running
- from M-file
- from the command line
- size of generated code
- stopping
- Simulink
- accessing
- configuring for DSP
- default settings
- description <1> <2>
- learning <1> <2>
- libraries <1> <2>
- parameters
simulink
- Sine Wave block <1> <2>
- in tutorial
- single-rate blocks
- single-rate models
- single-tasking mode <1> <2>
- Singular Value Decomposition block
- size
- of a frame
- See also frame sizes
- of a matrix
- of an array
- size of a vector
- defined
- See also frame sizes
- sliding windows
- example
- Solver options panel, recommended settings
Solver parameter
- solvers
- fixed-step
- variable-step
- Sort block
- sound
- exporting <1> <2> <3>
- importing <1> <2>
- source blocks
- defined
- sample periods of
- sources
- discrete-time
- sample periods of
- spectral analysis
- Burg method
- covariance method
- magnitude FFT method
- modified covariance method
- See also power spectrum estimation
- short-time FFT method
- Yule-Walker method
- Spectrum Scope block <1> <2>
- speed, improving <1> <2> <3>
- Stack block
- stack events <1> <2>
- standard deviation
- computing
- Standard Deviation block <1> <2>
startup M-file
startupsav M-file
- editing
- state-space forms <1> <2>
- statistics
- operations <1> <2>
- RMS
- standard deviation
- variance
- Statistics library
- stereo inputs
- Stereo parameter
- ST-FFT method
- stopband, attenuation
- stopping a simulation
StopTime parameter
- Submatrix block
- SVD Solver block
- swept cosine
- swept-frequency cosine
- switching
- between two inputs
- symbols, time and frequency
- T (signal period)
- defined
- See also sample periods and frame periods
- tasking latency
- defined
- example
- predicting
- tasking modes
- technical conventions
- terminology, time and frequency <1> <2>
- Tf (frame period)
- defined
- See also frame periods
- Tfi (input frame period)
- defined
- See also frame periods
- Tfo (output frame period)
- defined
- See also frame periods
- throughput rates, increasing
- Time check box
- Time Scope Block
- Time Scope block
- time-step vector, saving to workspace
- To Wave Device block <1> <2>
- To Wave File block <1> <2>
- Toeplitz block
tout vector, suppressing
- transforms
- discrete cosine
- discrete wavelet
- Fourier
- Transpose block
- transposing
- matrices
- trends, removing
- triangular windows
- triggered blocks
- Triggered Delay Line block
- Triggered Shift Register block
- initial state of
- Triggered Signal From Workspace block
- Triggered Signal To Workspace block
- triggering
- for N-Sample Enable block <1> <2>
- for Sample and Hold block
- for Triggered Shift Register block
- for Triggered Signal From Workspace block
- for Triggered Signal To Workspace block
- Ts (sample period)
- defined <1> <2>
- See also sample periods
- Tsi (input sample period)
- defined
- See also sample periods
- Tso (output sample period)
- defined
- See also sample periods
- tunable parameters
- Two-Channel Analysis Subband Filter block
- Two-Channel Synthesis Subband Filter block
- typographical conventions (table)
- Unbuffer block <1> <2> <3>
- initial state of
- unbuffering <1> <2> <3>
- and rate conversion
- frame-based signals
- partial
- to a sample-based signal
- Uniform Decoder block
- Uniform Encoder block <1> <2>
- units of time and frequency measures
- Unwrap block
- unwrapping radian phase angles
- Upsample block <1> <2> <3>
- upsampling <1> <2> <3> <4>
- by inserting zeros
- See also rate conversion
- utility functions
dsp_links
dsplib
dspstartup
rebuffer_delay
- Variable Fractional Delay block
- initial conditions for <1> <2>
- Variable Integer Delay block
- initial conditions for <1> <2>
- Variable Selector block <1> <2> <3> <4>
- variable-step solver <1> <2>
- variance <1> <2>
- tracking
- Variance block <1> <2>
- Vector Scope block <1> <2> <3>
- vectors
- 1-D
- converting to scalars
- creating
- by buffering
- from scalars
- defined
- displaying
- exporting
- importing <1> <2>
- versions
- displaying information about
- opening
- viewing data
- with scopes
- viewing in a model
- Wavelet Analysis block
- Wavelet Synthesis block
- Window Function block
- windows
- applying
- Bartlett
- Blackman
- Chebyshev <1> <2>
- computing
- Hamming
- Hann
- Kaiser <1> <2>
- rectangular
- triangular
- workspace
- importing data from
- suppressing output to
- Workspace I/O panel
yout, suppressing
- Yule-Walker Estimator block
- Yule-Walker Method block
- Zero Pad block <1> <2> <3>
- Zero-Order Hold block
- zero-padding <1> <2> <3>
- causing unintentional rate conversions
- zeros
- inserting <1> <2> <3>
- outputting
- Counter block
- Discrete Impulse block
- Integer Delay block
- N-Sample Enable block
- Signal From Workspace block <1> <2>
- padding with <1> <2>
 | Miscellaneous Settings | |


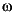 (digital frequency). See frequencies
(digital frequency). See frequencies
 (angular frequency). See frequencies
(angular frequency). See frequencies
 p (passband edge frequency)
p (passband edge frequency)
 p1 (lower passband edge frequency)
p1 (lower passband edge frequency)
 p2 (upper passband edge frequency)
p2 (upper passband edge frequency)
 s (stopband edge frequency)
s (stopband edge frequency)
 s1 (lower stopband edge frequency)
s1 (lower stopband edge frequency)
 s2 (upper stopband edge frequency)
s2 (upper stopband edge frequency)
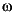 (digital frequency)
(digital frequency)
 (angular frequency)
(angular frequency)
 p (passband edge frequency)
p (passband edge frequency)
 p1 (lower passband edge frequency)
p1 (lower passband edge frequency)
 p2 (upper passband edge frequency)
p2 (upper passband edge frequency)
 s (stopband edge frequency)
s (stopband edge frequency)
 s1 (lower stopband edge frequency)
s1 (lower stopband edge frequency)
 s2 (upper stopband edge frequency)
s2 (upper stopband edge frequency)
