

| DSP Blockset |   |
Compute the variance of an input or sequence of inputs.
Library
Description
The Variance block computes the variance of each column in the input, or tracks the variance of a sequence of inputs over a period of time. The Running variance parameter selects between basic operation and running operation.
Basic Operation
When the Running variance check box is not selected, the block computes the variance of each column in M-by-N input matrix u independently at each sample time.
For convenience, length-M 1-D vector inputs and sample-based length-M row vector inputs are both treated as M-by-1 column vectors. (A scalar input generates a zero-valued output.)
The output at each sample time, y, is a 1-by-N vector containing the variance for each column in u. For purely real or purely imaginary inputs, the variance of the jth column is the square of the standard deviation:
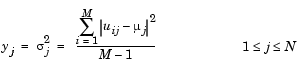
where µj is the mean of the jth column. For complex inputs, the output is the total variance for each column in u, which is the sum of the real and imaginary variances for that column:
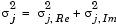
The frame status of the output is the same as that of the input.
Running Operation
When the Running variance check box is selected, the block tracks the variance of each channel in a time-sequence of M-by-N inputs. For sample-based inputs, the output is a sample-based M-by-N matrix with each element yij containing the variance of element uij over all inputs since the last reset. For frame-based inputs, the output is a frame-based M-by-N matrix with each element yij containing the variance of the jth column over all inputs since the last reset, up to and including element uij of the current input.
As in basic operation, length-M 1-D vector inputs and sample-based length-M row vector inputs are both treated as M-by-1 column vectors.
Resetting the Running Variance. The block resets the running variance whenever a reset event is detected at the optional Rst port. The reset signal rate must be a positive integer multiple of the rate of the data signal input.
The reset event is specified by the Reset port parameter, and can be one of the following:
Rst port.
Rst input does one of the following:
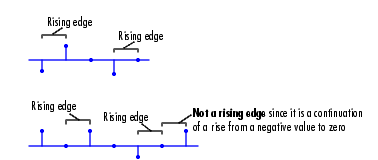
Rst input does one of the following:
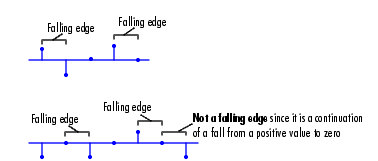
Rst input is a Rising edge or Falling edge (as described above).
Rst input is not zero.
| Note When running simulations in the Simulink MultiTasking mode, sample-based reset signals have a one-sample latency, and frame-based reset signals have one frame of latency. Thus, there is a one-sample or one-frame delay between the time the block detects a reset event, and when it applies the reset. For more information on latency and the Simulink tasking modes, see Excess Algorithmic Delay (Tasking Latency) and the topic on the Simulation Parameters dialog box in the Simulink documentation. |
Example
The Variance block in the model below calculates the running variance of a frame-based 3-by-2 (two-channel) matrix input, u. The running variance is reset at t=2 by an impulse to the block's Rst port.
The Variance block has the following settings:
The Signal From Workspace block has the following settings:
The Discrete Impulse block has the following settings:
The block's operation is shown in the figure below.
The statsdem demo illustrates the operation of several blocks from the Statistics library.
Dialog Box
Supported Data Types
Rst port.
To learn how to convert to the above data types in MATLAB and Simulink, see Supported Data Types and How to Convert to Them.
See Also
| Mean |
DSP Blockset |
| RMS |
DSP Blockset |
| Standard Deviation |
DSP Blockset |
var |
MATLAB |
Also see Statistics for a list of all the blocks in the Statistics library.
 | Variable Selector | Vector Scope |  |