| SimMechanics |
  |
Custom Joint
Represent a customizable composite joint with up to three translational and three rotational degrees of freedom
Library
Joints
Description
The Custom Joint block is a composite joint that you can customize with a specified combination of primitives (prismatic, revolute, or spherical) representing the most general and unconstrained degrees of freedom (DoFs) in three dimensions:
- Up to three translational DoFs as three prismatic primitives
- Up to three rotational DoFs:
- As a single spherical primitive
- As two or three revolute primitives
- The sense of rotational DoFs is defined by the right-hand rule. One spherical or three revolutes together form a right-handed system.
You can add, configure, and delete these primitives from the Custom Joint, with a minimum and default of one primitive. The properties of each primitive are the same as the individual Joints of the same names.
| Caution
A joint with two or three revolute primitives becomes singular if two or three of the rotation axes become parallel ("gimbal lock"). A joint with two or three prismatic primitives becomes singular if two or three of the translation axes become parallel. The simulation stops with errors in these cases.
|
The Custom Joint block's primitives are assembled: you must connect each side of the Joint block to a Body block at a Body coordinate system (CS) point, and the origins of these Body CSs must be spatially collocated points, within assembly tolerances.
You can connect the Custom Joint to Actuator and Sensor blocks, with each Actuator and Sensor connecting to an individual primitive. You cannot connect a spherical primitive to an Actuator block.
You can connect any Joint block to two and only two Body blocks, and Joints have a default of two Connector Ports for connecting to base and follower Bodies.
Any Joint block represents only the abstract relative motion of two bodies, not the bodies themselves. You must specify a reference CS to define the direction of the joint axes.
Dialog Box and Parameters
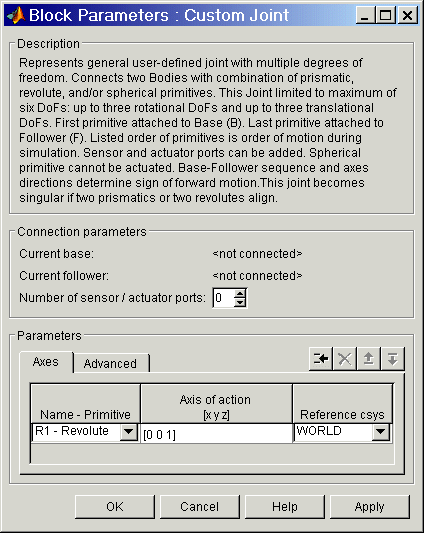
The dialog box has two active areas, Connection parameters and Parameters.
Connection Parameters
- Current base
- When you connect the base (B) Connector Port on the Custom Joint block to a Body CS Port on a Body, this parameter is automatically reset to the name of this Body CS. See the following Custom Joint base and follower Body Connector Ports figure.
- The base Body is automatically connected to the first joint primitive in the primitive list in Parameters.
- Current follower
- When you connect the follower (F) Connector Port on the Custom Joint block to a Body CS Port on a Body, this parameter is automatically reset to the name of this Body CS. See the following Custom Joint base and follower Body Connector Ports figure.
- The follower Body is automatically connected to the last joint primitive in the primitive list in Parameters.
- Number of sensor/actuator ports
- Using this spinner menu, you can set the number of extra Connector Ports needed for connecting Joint Actuator and Joint Sensor blocks to this Joint. The default is
0. A spherical primitive cannot be connected to an Actuator.
- The motion of a prismatic primitive is specified in linear units. The motion of a revolute primitive is specified in angular units. The motion of a spherical primitive is three DoFs specified in quaternion form.
The base (B)-follower (F) Body sequence determines the sense of positive motion:
- Positive translation is the follower moving in the direction of the translation axis.
- Positive rotation is the follower rotating in the right-handed sense about the rotation axis.
- Positive rotation is the follower rotating in the right-handed sense as shown in the Spherical block figure.
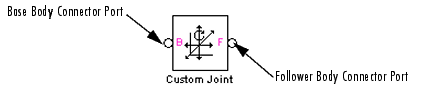
Custom Joint base and follower Body Connector Ports
Parameters
Toggle between the Axes and Advanced panels with the tabs.
The entries on the Axes pane are required. Each DoF primitive in Custom Joint has an entry line. These lines specify the direction of the axes of action of the DoFs that the Custom Joint represents.
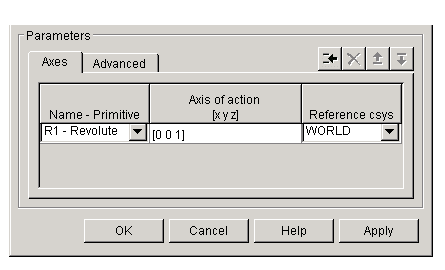
- Name - Primitive
- In the pull-down menu, select a label and primitive type for this DoF. Up to three prismatic primitives
P1, P2, P3 are allowed. The rotational DoFs are represented by up to three revolute primitives: R1, R2, R3. A spherical primitive S can take all three allowed rotational DoFs instead.
- The default value is
R1 - Revolute.
- Axis of action [x y z]
- Enter here as a three-component vector the directional axis defining the allowed motion of this primitive and its corresponding DoF:
- Prismatic: axis of translation
- Revolute: axis of rotation
- Spherical: field is not active
- The default vector is
[0 0 1]. The axis is a directed vector whose overall sign matters.
- To prevent singularities and simulation errors, no two of the revolute axes and no two of the prismatic axes can be parallel.
- Reference csys
- Using the pull-down menu, choose the coordinate system (World, the base Body CS, or the follower Body CS) whose coordinate axes the vector axis of action is oriented with respect to. This CS also determines the absolute meaning of forces/torques and motion along/about the joint axis. The default is
WORLD.
- The field is not active for a spherical primitive.
Managing the Joint Primitives List in a Custom Joint
The Custom Joint primitives list controls (see the following Custom Joint primitives list controls figure) allow you to add, reorder, and delete joint primitives in a Custom Joint block:
- To add a joint primitive to the primitives list:
- To change the position of a joint primitive in the list:
- Highlight the primitive whose position you want to change.
- Click on the Up or Down button (see the following Custom Joint primitives list controls figure) until the primitive is where you want it.
- To delete a joint primitive from the list:
- Custom Joint requires at least one primitive, which you cannot delete.
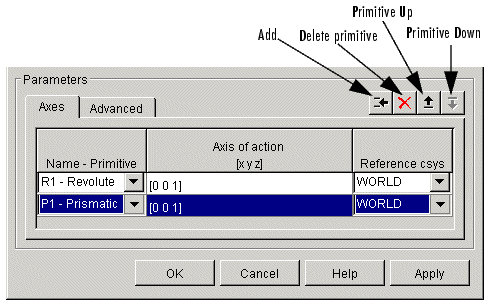
Custom Joint primitives list controls
The Advanced pane is optional. You use it to control the way SimMechanics interprets the topology of your schematic diagram.

- Mark as the preferred cut joint
- In a closed loop, one and only one joint is cut during the simulation. SimMechanics does the cutting internally and automatically.
- If you want this particular joint to be weighted preferentially for cutting during the simulation, select the check box. The default is unselected.
See Also
Bushing, Gimbal, Joint Actuator, Joint Initial Condition Actuator, Joint Sensor, Joint Stiction Actuator, Prismatic, Revolute, Six-DoF, Spherical
See Modeling Joints for more on representing DoFs with Joints.
See Checking Schematic Topology and How SimMechanics Works for more on closed loops and cutting.
 | Continuous Angle | | Cylindrical |  |