
| SimMechanics |   |
Represent a prismatic joint with one translational degree of freedom
Library
Description
The Prismatic block represents a single translational degree of freedom (DoF) along a specified axis between two bodies. A prismatic joint is one of SimMechanics primitive joints, along with revolute and spherical.
The Prismatic block is assembled: you must connect each side of the Joint block to a Body block at a Body coordinate system (CS) point, and the origins of these Body CSs must lie along the prismatic axis, to within assembly tolerances. These Body CS origins do not need to be collocated in space.
You can connect any Joint block to two and only two Body blocks, and Joints have a default of two Connector Ports for connecting to base and follower Bodies.
A Joint block represents only the abstract relative motion of two bodies, not the bodies themselves. You must specify a reference CS to define the direction of the joint axis.
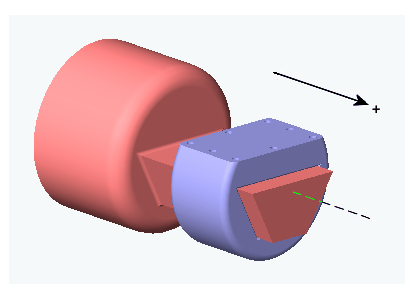
Prismatic motion of follower (blue) relative to base (red)
Dialog Box and Parameters
The dialog box has two active areas, Connection parameters and Parameters.
Connection Parameters
0.The base (B)-follower (F) Body sequence determines the sense of positive motion. Positive translation is the follower moving in the direction of the translation axis.
Prismatic base and follower Body Connector Ports
Parameters
Toggle between the Axes and Advanced panels with the tabs.
The entries on the Axes pane are required. They specify the direction of the translational DoF that the Prismatic represents.
P1.Prismatic.[0 0 1]. The axis is a directed vector whose overall sign matters.WORLD.The Advanced pane is optional. You use it to control the way SimMechanics interprets the topology of your schematic diagram.
See Also
Disassembled Prismatic, Joint Actuator, Joint Initial Condition Actuator, Joint Sensor, Joint Stiction Actuator, Revolute, Spherical
See Modeling Joints for more on representing DoFs with Joints.
See Checking Schematic Topology and How SimMechanics Works for more on closed loops and cutting.
 | Point-Curve Constraint | Revolute |  |