

| Mu Analysis and Synthesis Toolbox |   |
Compute an H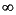 controller for a SYSTEM interconnection matrix that minimizes the entropy integral at a specific frequency
controller for a SYSTEM interconnection matrix that minimizes the entropy integral at a specific frequency
Syntax
Description
hinfsyne is a variation of hinfsyn and calculates an H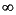 controller that achieves the infinity norm
controller that achieves the infinity norm gfin for the interconnection structure p. The controller, k, stablizes the SYSTEM matrix p and has the same number of states as p. Of the controllers achieving this norm bound, k is chosen to minimize an entropy integral relating to the point s0; i.e.,
where g is the closed-loop transfer function. In addition, the amount of printing on the screen can be controlled.
Note that the outputs ax, ay, hamx, and hamy correspond to scaled or balanced data.
The hinfsyne program outputs several variables, which can be checked to ensure that the above conditions are being met. For each 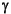 value the minimum magnitude, real part of the eigenvalues of the X Hamiltonian matrices is displayed along with the minimum eigenvalue of X
value the minimum magnitude, real part of the eigenvalues of the X Hamiltonian matrices is displayed along with the minimum eigenvalue of X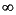 , which is the solution to the X Riccati equation. A # sign is placed to the right of the condition that failed in the printout. This additional information can aid you in the control design process.
, which is the solution to the X Riccati equation. A # sign is placed to the right of the condition that failed in the printout. This additional information can aid you in the control design process.
Algorithm
hinfsyne uses the formulas similar to the ones described in the Glover and Doyle paper for solution to the H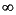 control design problem. See the
control design problem. See the hinfsyn command for more information.
hinf_st, hinf_gam, hinfe_c, hinf_gam calls: ric_eig, ric_schr, csord, and cgivens
Reference
Doyle, J.C., K. Glover, P. Khargonekar, and B. Francis, "State-space solutions to standard H2 and H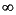 control problems," IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol. 34, no. 8, pp. 831-847, August 1989.
control problems," IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, vol. 34, no. 8, pp. 831-847, August 1989.
Glover, K., and J.C. Doyle, "State-space formulae for all stabilizing controllers that satisfy an H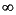
norm bound and relations to risk sensitivity," Systems and Control Letters, vol. 11, pp. 167-172, 1988.
See Also
dhfsyn, hinfsyn, hinffi, hinfnorm, h2syn, h2norm, ric_eig, ric_schr, sdhfsyn
 | hinfsyn | indvcmp |  |