| MATLAB Function Reference |   |
表示
x = cgs(A,b) cgs(A,b,tol) cgs(A,b,tol,maxit) cgs(A,b,tol,maxit,M) cgs(A,b,tol,maxit,M1,M2) cgs(A,b,tol,maxit,M1,M2,x0) cgs(afun,b,tol,maxit,m1fun,m2fun,x0,p1,p2,...) [x,flag] = cgs(A,b,...) [x,flag,relres] = cgs(A,b,...) [x,flag,relres,iter] = cgs(A,b,...) [x,flag,relres,iter,resvec] = cgs(A,b,...)
詳細
x = cgs(A,b)
は、xに関する線形方程式A*x = bを解きます。n行n列の係数行列 A は、正方で、列ベクトルb は、長さ nである必要があります。A は、afun(x) が、A*xを出力するような関数afunです。
cgs が収束する場合、その影響に関するメッセージが表示されます。cgsが、設定した繰り返し最大回数に達した後や、何らかの理由で、収束しない場合、相対残差 norm(b-A*x)/norm(b)とこの方法が停止した時点での繰り返し回数を表すワーニングメッセージが表示されます。
cgs(A,b,tol)
は、この方法で使用できる許容誤差範囲 tolを設定できます。 tolが、[]の場合、cgs は、デフォルト値 1e-6を使います。
cgs(A,b,tol,maxit)
は、最大繰り返し回数 maxit を指定します。maxit が、[] の場合、cgs は、デフォルト min(n,20) を使います。
cgs(A,b,tol,maxit,M) と cgs(A,b,tol,maxit,M1,M2)
は、左側の前提条件M、または、code>M = M1*M2を使い、システムinv(M)*A*x = inv(M)*bを xについて効率良く解きます。M1またはM2が空行列([])ならば、前提条件は適用されません(それらが単位行列であることと等価です)。cgsで、M*y = rの型の方程式をバックスラッシュを使って解くときに、前提条件を最初のLU因子に分解するのが望ましいです。たとえば、cgs(A,b,tol,maxit,M)を、つぎのステートメントで置き換えます。
cgs(A,b,tol,maxit,M1,M2,x0)
は、初期推定x0を指定します。x0が空行列([])ならば、デフォルトの全要素がゼロのベクトルが使われます。
cgs(afun,b,tol,maxit,m1fun,m2fun,x0,p1,p2,...)
は、パラメータ p1,p2,... を関数 afun(x,p1,p2,...)、m1fun(x,p1,p2,...)、 m2fun(x,p1,p2,...)に渡します。
[x,flag] = cgs(A,b,...)
は、解 x とcgsの収束を記述するフラグを表示します。
flag が 0でない場合、戻される解 x は、すべての繰り返しを通して計算された最小ノルム残差です。flag 出力が設定されている場合、メッセージは表示されません。
[x,flag,relres] = cgs(A,b,...)
also returns the relative residual norm(b-A*x)/norm(b). If flag is 0, then relres 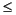
tol.
[x,flag,relres,iter] = cgs(A,b,...)
also returns the iteration number at which x was computed, where 0 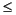
iter 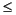
maxit.
[x,flag,relres,iter,resvec] = cgs(A,b,...)
also returns a vector of the residual norms at each iteration, including norm(b-A*x0).
例題
A = gallery('wilk',21);
b = sum(A,2);
tol = 1e-12; maxit = 15;
M1 = diag([10:-1:1 1 1:10]);
x = cgs(A,b,tol,maxit,M1,[],[]);
Alternatively, use this matrix-vector product function
function y = afun(x,n) y = [ 0; x(1:n-1)] + [((n-1)/2:-1:0)'; (1:(n-1)/2)'] .*x + [x(2:n); 0 ];
and this preconditioner backsolve function
function y = mfun(r,n) y = r ./ [((n-1)/2:-1:1)'; 1; (1:(n-1)/2)'];
x1 = cgs(@afun,b,tol,maxit,@mfun,[],[],21);
注意 that both afun and mfun must accept cgs's extra input n=21.
load west0479 A = west0479 b = sum(A,2) [x,flag] = cgs(A,b)
flag is 1 because cgs does not converge to the default tolerance 1e-6 within the default 20 iterations.
[L1,U1] = luinc(A,1e-5) [x1,flag1] = cgs(A,b,1e-6,20,L1,U1)
flag1 is 2 because the upper triangular U1 has a zero on its diagonal, and cgs fails in the first iteration when it tries to solve a system such as U1*y = r for y with backslash.
[L2,U2] = luinc(A,1e-6) [x2,flag2,relres2,iter2,resvec2] = cgs(A,b,1e-15,10,L2,U2)
flag2 is 0 because cgs converges to the tolerance of 6.344e-16 (the value of relres2) at the fifth iteration (the value of iter2) when preconditioned by the incomplete LU factorization with a drop tolerance of 1e-6. resvec2(1) = norm(b) and resvec2(6) = norm(b-A*x2). You can follow the progress of cgs by plotting the relative residuals at each iteration starting from the initial estimate (iterate number 0) with
semilogy(0:iter2,resvec2/norm(b),'-o')
xlabel('iteration number')
ylabel('relative residual')
参考
bicg, bicgstab, gmres, lsqr, luinc, minres, pcg, qmr, symmlq
@ (function handle), \ (backslash)
参考文献
Barrett, R., M. Berry, T. F. Chan, et al., Templates for the Solution of Linear Systems: Building Blocks for Iterative Methods, SIAM, Philadelphia, 1994.
Sonneveld, Peter, "CGS: A fast Lanczos-type solver for nonsymmetric linear systems", SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput., January 1989, Vol. 10, No. 1, pp. 36-52.
 | cellstr | char |  |