| Robust Control Toolbox |   |
H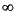 optimal control synthesis via
optimal control synthesis via 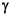 -iteration.
-iteration.
Syntax
[gamopt,acp,,dcp,acl,,dcl] = hinfopt(A,,D22) [gamopt,acp,,dcp,acl,,dcl] = hinfopt(A,,D22,gamind) [gamopt,acp,,dcp,acl,,dcl] = hinfopt(A,,D22,gamind,aux) [gamopt,sscp,sscl] = hinfopt(tss) [gamopt,sscp,sscl] = hinfopt(tss,gamind) [gamopt,sscp,sscl] = hinfopt(tss,gamind,aux)
Description
hinfopt does H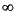 "
"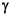 -iteration" to compute the optimal H
-iteration" to compute the optimal H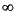 controller using the loop-shifting two-Riccati formulae of
controller using the loop-shifting two-Riccati formulae of hinf. The output gamopt is the optimal "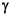 " for which the cost function
" for which the cost function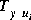 can achieve under a preset tolerance
can achieve under a preset tolerance
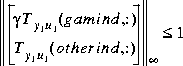
An optional input variable aux specifies the tolerance that stops the  -iteration
-iteration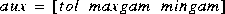
where maxgam and mingam denotes a range for 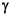 -iteration to be carried out. The default value of
-iteration to be carried out. The default value of aux is [0.01 1 0]. Another optional input variable gamind specifies the indices of the cost function output channels (i.e.,rows) to be scaled by 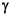 . Default for
. Default for gamind is to scale all the output channels (gamind = 1: n).
Algorithm
A binary search algorithm is coded in hinfopt to achieve the required 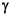 -iteration. The iteration logic is based on the H
-iteration. The iteration logic is based on the H existence tests performed inside
existence tests performed inside hinf and recorded in the output variable hinfo of hinf. The search of optimal 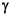 stops whenever the
stops whenever the 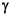 relative error between two adjacent stable solutions is less than the tolerance specified. For most practical purposes, the tolerance can be set at 0.01 or 0.001.
relative error between two adjacent stable solutions is less than the tolerance specified. For most practical purposes, the tolerance can be set at 0.01 or 0.001.
Examples
Following are three simple problems solved via hinfopt with the SISO plant 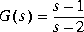
Problem 1: Mixed-Sensitivity
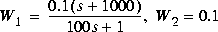 , no W3.
, no W3.
[ag,bg,cg,dg] = tf2ss([1 -1],[1 -2]); ssg = mksys(ag,bg,cg,dg); w1 = [0.1*[1 100];[100 1]]; w2 = [0.1;1]; w3 = []; [TSS] = augtf(ssg,w1,w2,w3); [gamopt,sscp,sscl] = hinfopt(TSS,[1:2],[0.001,1,0]);
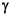 opt = 1.5146.
In this case,
opt = 1.5146.
In this case, 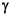 opt = 2.5, F(s) = -4/3.
opt = 2.5, F(s) = -4/3.
w1 = [1 1;10 1]; w2 = []; [TSS] = augtf(ssg,w1,w2,w3); [gamopt,sscp,sscl] = hinfopt(TSS,1,[0.001,1,0]);
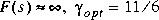 .
.
These three very simple problems can be also solved analytically using the interpolation technique of [1], augmented in the case of problem 1 with the "two-block to one-block" embedding technique of [2]. The results of hinfopt match the exact solutions very well.
See Also
augss, augtf, hinf, linf
References
[1] G. Zames and B. A. Francis, "Feedback, Minimax Sensitivity, and Optimal Robustness," IEEE Trans. on Autom. Control, AC-28, 5, pp. 585-601, May 1983.
[2] M. Verma and E. A. Jonckheere, "L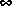 -Compensation with Mixed Sensitivity as a Broadband Matching Problem," Systems and Control Letters, 4, pp. 125-129, May 1984.
-Compensation with Mixed Sensitivity as a Broadband Matching Problem," Systems and Control Letters, 4, pp. 125-129, May 1984.
 | hinf, dhinf, linf | imp2ss |  |