| SimPowerSystems |   |
Session 5: Simulating Motor Drives
Variable speed control of AC electrical machines makes use of forced-commutated electronic switches such as IGBTs, MOSFETs, and GTOs. Asynchronous machines fed by pulse width modulation (PWM) inverters are now gradually replacing the DC motors and thyristor bridges. With PWM associated with modern control techniques such as field-oriented control or direct torque control, it is now possible to obtain the same flexibility in speed and torque control as with DC machines. In this session you build a simple open loop DC drive controlling an asynchronous machine. A more elaborate example of a PWM drive is presented in the Case Studies chapter. The Power System Blockset circuit to simulate is shown in Figure 1-13. It uses blocks of the Machines and Power Electronics libraries.
The Machines library contains four of the most commonly used three-phase machines: simplified and complete synchronous machines, asynchronous machine, and permanent magnet synchronous machine. Each machine can be used either in generator or motor mode. Combined with linear and nonlinear elements such as transformers, lines, loads, breakers, etc., they can be used to simulate electromechanical transients in an electrical network. They can also be combined with power electronic devices to simulate drives.
The Power Electronics library contains blocks allowing you to simulate diodes, thyristors, GTO thyristors, MOSFETs, and IGBT devices. You could interconnect several blocks together to build a three-phase bridge. For example, an IGBT inverter bridge would require six IGBTs and six antiparallel diodes.
In order to facilitate implementation of bridges, the Universal Bridge block automatically performs these interconnections for you.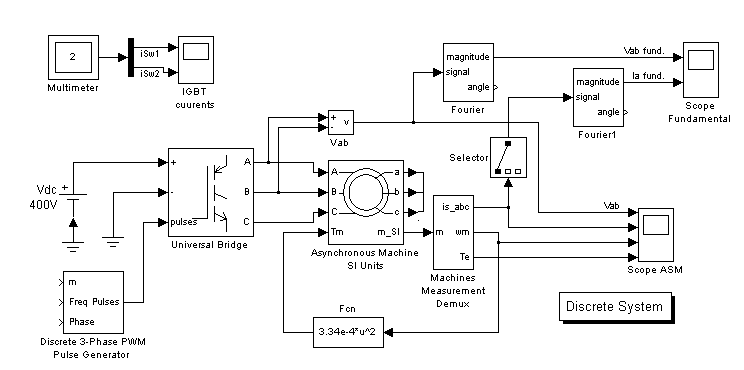
Figure 1-13: Circuit 5: PWM Control of an Induction Motor
 | Session 4: Introducing Power Electronics | Building and Simulating the PWM Motor Drive |  |