| SimPowerSystems |   |
Modeling the Induction Motor Drive
Open the psbacdrive model and save it as case4.mdl in your working directory so that you can make further modifications without altering the original file.
The next figure shows the psbacdrive model in which blocks from Power System Blockset and Simulink are used to model the induction motor drive.
Figure 2-23: Variable-Speed Field-Oriented Induction Motor Drive (psbacdrive.mdl)
The induction motor is modeled by an Asynchronous Machine block. The motor used in this case study is a 50 HP, 460 V, four-pole, 60 Hz motor having the following parameters: Rs = 0.087 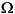
, Lls = 0.8 mH, Lm = 34.7 mH, Rr = 0.228 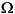
, Llr = 0.8 mH.
The current-controlled PWM inverter circuit is shown in Figure 2-23. The IGBT inverter is modeled by a Universal Bridge block in which the Power Electronic device and Port configuration options are selected as IGBT/Diode and ABC as output terminals respectively. The DC link input voltage is represented by a 780 V DC voltage source.
The current regulator, which consists of three hysteresis controllers, is built with Simulink blocks. The motor currents are provided by the measurement output of the Asynchronous Machine block.
The conversions between abc and dq reference frames are executed by the abc_dq and dq_abc blocks of Figure 2-23.
The rotor flux is calculated by the Flux_Calculation block of Figure 2-23.
The rotor flux position (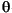 e) is calculated by the Teta Calculation block of Figure 2-23.
e) is calculated by the Teta Calculation block of Figure 2-23.
The stator quadrature-axis current reference (iqs*) is calculated by the iqs*_Calculation block of Figure 2-23.
The stator direct-axis current reference (ids*) is calculated by the id*_Calculation block of Figure 2-23.
The speed controller is of proportional-integral type and is implemented using Simulink blocks.
 | A Field-Oriented Variable-Speed Induction Motor Drive | Simulating the Induction Motor Drive |  |