| SimPowerSystems |   |
A Field-Oriented Variable-Speed Induction Motor Drive
This case study illustrates a variable-speed induction motor drive using field-oriented control. In this control scheme, a dq coordinates reference frame locked to the rotor flux space vector is used to achieve decoupling between the motor flux and torque. They can thus be controlled separately by stator direct-axis current and quadrature-axis current respectively, as in a DC motor. This figure shows a block diagram of a field-oriented induction motor drive:
Figure 2-21: Field-Oriented Variable-Frequency Induction Motor Drive
The induction motor is fed by a current-controlled PWM inverter, which operates as a three-phase sinusoidal current source. The motor speed 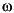 is compared to the reference
is compared to the reference 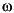 * and the error is processed by the speed controller to produce a torque command Te*.
* and the error is processed by the speed controller to produce a torque command Te*.
As shown below, the rotor flux and torque can be separately controlled by the stator direct-axis current ids and quadrature-axis current iqs, respectively.
Figure 2-22: Field-Oriented Control Principle
The stator quadrature-axis current reference iqs* is calculated from torque reference Te* as
where Lr is the rotor inductance, Lm is the mutual inductance, and |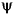 r|est is the estimated rotor flux linkage given by
r|est is the estimated rotor flux linkage given by
where 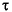 r = Lr / Rr is the rotor time constant.
r = Lr / Rr is the rotor time constant.
The stator direct-axis current reference ids* is obtained from rotor flux reference input |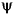 r|*:
r|*:
The rotor flux position 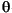 e required for coordinates transformation is generated from the rotor speed
e required for coordinates transformation is generated from the rotor speed 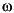 m and slip frequency
m and slip frequency 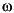 sl:
sl:
The slip frequency is calculated from the stator reference current iqs* and the motor parameters.
The iqs* and ids* current references are converted into phase current references ia*, ib*, ic* for the current regulators. The regulators process the measured and reference currents to produce the inverter gating signals.
The role of the speed controller is to keep the motor speed equal to the speed reference input in steady state and to provide a good dynamic during transients. It can be of proportional-integral type.
 | Variable-Frequency Induction Motor Drive | Modeling the Induction Motor Drive |  |