

| Mu Analysis and Synthesis Toolbox |   |
Augment CONSTANT, SYSTEM and VARYING matrices
Syntax
Description
abv places the matrix mat1 above the matrix mat2. daug places the input matrices on the diagonal of the output matrix. sbs places the input matrices next to one another. All these commands, abv, daug, and sbs, allow the use of multiple input arguments inputs (up to nine). CONSTANT, SYSTEM, and VARYING matrices can be placed by one another based on the following table:
mat1
|
mat2
| |||
| CONSTANT |
SYSTEM |
VARYING |
||
| CONSTANT |
yes |
yes |
yes |
|
| SYSTEM |
yes |
yes |
no |
|
| VARYING |
yes |
no |
yes |
|
The input matrices must be compatible in the respective dimension in order for the function to be performed. abv requires the same number of columns (inputs for SYSTEM matrices) and sbs requires the input matrices to have the same number of rows (outputs for SYSTEM matrices).
Pictorial Representation of Functions
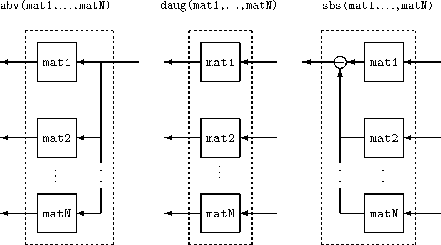
Examples
Create two CONSTANT matrices a and b along with two SYSTEM matrices p1 and p2. Examples of manipulation using abv, daug, and sbs are shown in the following examples:
a = [1 2 3; 4 5 6]; b = [7 7 7; 8 8 8 ]; pl = pck(-10,1,10,0); p2 = pck(-3,2,4,.1), seesys(abv(p1,p2))-1.0e+01 0.0e+00 | 1.0e+000.0e+00 -3.0e+00 | 2.0e+00 --------------------------------- 0.0e+01 0.0e+00 | 0.0e+00 0.0e+01 4.0e+00 | 1.0e-00out = abv(a,b,b)out =1 2 34 5 67 7 78 8 87 7 78 8 8out = daug(a,b)out= 1 2 3 0 0 0 4 5 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 7 7 7 0 0 0 8 8 8
out=sbs(p1,p2); seesys =out-1.0e+01 0.0e+00 | 1.0e+00 0.0e+000.0e+00 -3.0e+00 | 0.0e+002.0e+00-------------------------------------------- 1.0e+01 4.0e+00 | 0.0e+001.0e-01minfo(out) system:2states1 outputs2 inputsout=sbs(a,b,a)out= 1 2 3 7 7 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 8 8 4 5 6
See Also
madd, mmult, sel, vdiag
 | Reference | blknorm |  |