| Data Acquisition Toolbox |   |
Extracting Data from the Engine
Many data acquisition applications require that data is acquired at a fixed (often high) rate, and that the data is processed in some way immediately after it is collected. For example, you might want to perform an FFT on the acquired data and then save it to disk. When processing data, you must extract it from the engine. If acquired data is not extracted in a timely fashion, it can be overwritten.
Data is extracted from the engine with the getdata function. For example, to extract 1000 samples for the analog input object ai:
In addition to returning acquired data, getdata can return relative time, absolute time, and event information. As shown below, data is an m-by-n array containing acquired data where m is the number of samples and n is the number of channels.
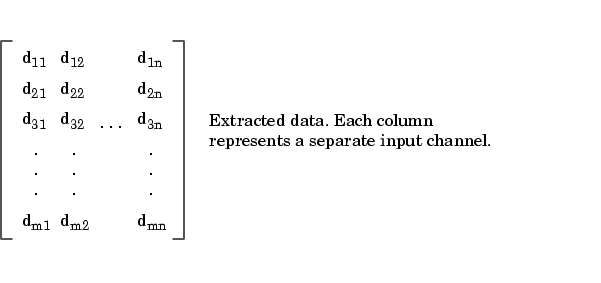
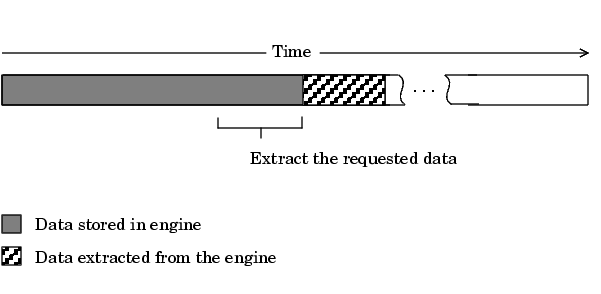
getdata is considered a blocking function because it returns control to MATLAB only when the requested data is available. Therefore, samples are not missed or repeated. When a trigger executes, acquired data fills the engine. When a getdata call is processed, the requested samples are returned when the data is available, and then extracted from the engine.
As shown below, if a fraction of the data stored in the engine is extracted, then getdata always extracts the oldest data.
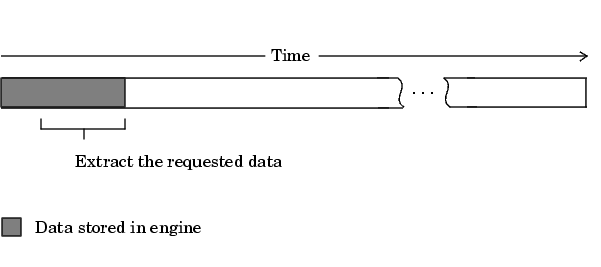
If another getdata call is issued, then once again, the oldest samples are extracted.
Rules for Using getdata
Using getdata to extract data stored in the engine follows these rules:
Timeout property.
getdata is blocking. This will not stop the acquisition but will return control to MATLAB.
SamplesAcquired property keeps a running count of the total number of samples per channel that have been acquired.
SamplesAvailable property tells you how many samples you can extract from the engine per channel.
For more information about getdata, refer to its reference pages in Function Reference.
Example: Previewing and Extracting Data
Suppose you have a data acquisition application that is particularly time consuming. By previewing the data, you can ascertain whether the acquisition is proceeding as expected without acquiring all the data. If it is not, then you can abort the session and diagnose the problem. This example illustrates how you might use peekdata and getdata together in such an application.
You can run this example by typing daqdoc5_2 at the MATLAB command line.
AI for a sound card. The installed adaptors and hardware IDs are found with daqhwinfo.
AI.
P. The amount of data to display is given by preview.
duration = 10; % Ten second acquisition set(AI,'SampleRate',8000) ActualRate = get(AI,'SampleRate'); set(AI,'SamplesPerTrigger',duration*ActualRate) preview = duration*ActualRate/100; subplot(211) set(gcf,'doublebuffer','on') P = plot(zeros(preview,1)); grid on title('Preview Data') xlabel('Samples') ylabel('Signal Level (Volts)')
AI and update the display using peekdata every time an amount of data specified by preview is stored in the engine by polling SamplesAcquired. The drawnow command forces MATLAB to update the plot. After all data is acquired, it is extracted from the engine. Note that whenever peekdata is used, all acquired data might not be displayed.
AI, you should remove it from memory and from the MATLAB workspace.
 | Previewing Data | Returning Time Information |  |