| Communications Blockset |   |
Components of the Gray Coding Demo
This section discusses the purpose, behavior, and relevant parameters of each top-level component within the demo model. This section covers components in the order in which they process data in the simulation.
Random Integer Generator
The Random Integer Generator block produces random data that is used as the information in this simulation. This block generates one 100-symbol frame of integers in the range 0 to M-1 every Tsym seconds.
Integer-to-Bit Conversion
The Integer to Bit Converter block converts integer symbols to their equivalent binary representations. Its parameter is the number of bits in each integer.
Gray Coded M-PSK Modulation
The M-PSK Modulator Baseband block:
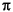 (M-1)/M
(M-1)/M
The table indicates which binary representations in the input correspond to which phasors in the output. The second column of the table is an intermediate representation that the block uses in its computations.
| Modulator Input |
Gray-Coded Ordering |
Modulator Output |
| 000 |
0 |
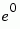 |
| 001 |
1 |
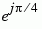 |
| 010 |
3 |
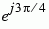 |
| 011 |
2 |
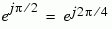 |
| 100 |
7 |
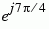 |
| 101 |
6 |
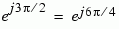 |
| 110 |
4 |
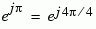 |
| 111 |
5 |
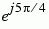 |
The table below sorts the first two columns of the table above, according to the output values. This sorting makes it clearer that the overall effect of this subsystem is a Gray code mapping as shown in the figure below. Notice that the numbers in the second column of the table below appear in counterclockwise order in the figure.
| Modulator Output |
Modulator Input |
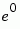 |
000 |
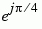 |
001 |
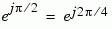 |
011 |
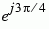 |
010 |
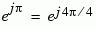 |
110 |
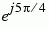 |
111 |
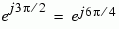 |
101 |
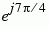 |
100 |
AWGN Channel
The AWGN Channel library block simulates transmission over a noisy channel. Its Signal to noise ratio (Es/No) mode uses these quantities to determine the variance:
The values for these parameters are chosen as follows:
EbNodB and M. The conversion from bit energy to symbol energy reflects the fact that each symbol carries log2(M) bits of information.
Tsym.
Gray Coded MPSK Demodulation
The M-PSK Demodulator Baseband block mirrors the Gray-coded modulation process. Notice that corresponding parameters in the modulator and demodulator blocks have the same values.
Bit-to-Integer Conversion
The Bit to Integer Converter block converts binary representations of symbols to their integer equivalents. Its parameter is the number of bits in each integer.
Error Rate Calculation
The Error Rate Calculation block compares demodulated symbols to original source symbols to compute the error rate. This model uses two Error Rate Calculation blocks, one to compute the symbol error rate and the other to compute the bit error rate. Both blocks use the parameter values shown below.
Symbol Error Details and Bit Error Details
Simulink's Display block shows the running error statistics throughout the simulation. Each Display block in the diagram lists three numbers, which represent:
Sending Data to the MATLAB Workspace
Simulink's To Workspace block sends the complete set of error statistics to the MATLAB workspace. When the simulation ends, the MATLAB variables SER and BER are both three-column matrices whose columns represent these quantities at each time step:
 | Variables in the Model | Learning More About the Gray Coding Demo |  |