| Writing S-Functions |   |
The MEX S-Function Wrapper
Creating S-functions using an S-function wrapper allows you to insert your C code algorithms in Simulink and the Real-Time Workshop with little or no change to your original C code function. A MEX S-function wrapper is an S-function that calls code that resides in another module. In effect, the wrapper binds your code to Simulink. A TLC S-function wrapper is a TLC file that specifies how the Real-Time Workshop should call your code (the same code that was called from the C-MEX S-function wrapper).
Suppose you have an algorithm (i.e., a C function), called my_alg that resides in the file my_alg.c. You can integrate my_alg into Simulink by creating a MEX S-function wrapper (e.g., wrapsfcn.c). Once this is done, Simulink will be able to call my_alg from an S-function block. However, the Simulink S-function contains a set of empty functions that Simulink requires for various API-related purposes. For example, although only mdlOutputs calls my_alg, Simulink calls mdlTerminate as well, even though this S-function routine performs no action.
You can integrate my_alg into the Real-Time Workshop generated code (i.e., embed the call to my_alg in the generated code) by creating a TLC S-function wrapper (e.g., wrapsfcn.tlc). The advantage of creating a TLC S-function wrapper is that the empty function calls can be eliminated and the overhead of executing the mdlOutputs function and then the my_alg function can be eliminated.
Wrapper S-functions are useful when creating new algorithms that are procedural in nature or when integrating legacy code into Simulink. However, if you want to create code that is:
then you must create a fully inlined TLC file for your S-function.
This figure illustrates the wrapper S-function concept.
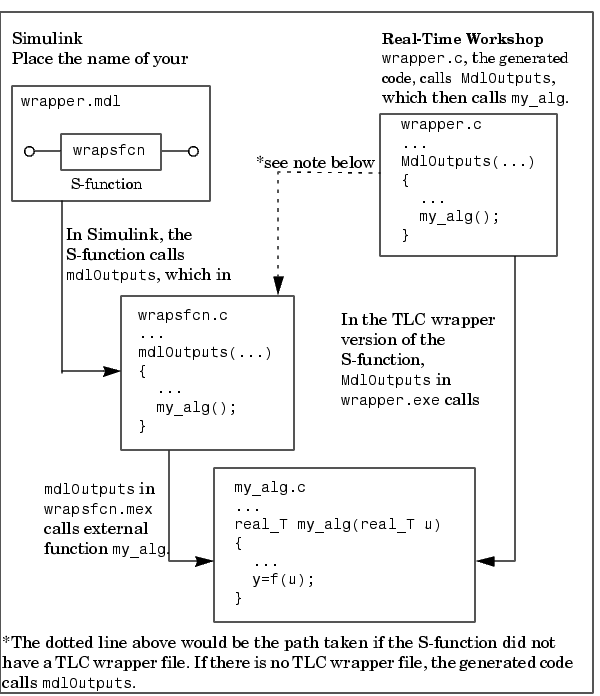
Figure 8-1: How S-Functions Interface with Hand-Written Code
Using an S-function wrapper to import algorithms in your Simulink model means that the S-function serves as an interface that calls your C code algorithms from mdlOutputs. S-function wrappers have the advantage that you can quickly integrate large stand-alone C code into your model without having to make changes to the code.
This is an example of a model that includes an S-function wrapper.
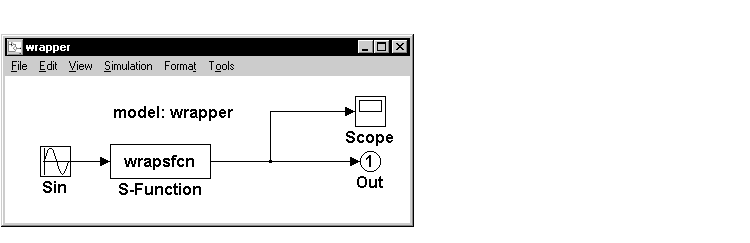
Figure 8-1: An Example Model That Includes an S-Function Wrapper
There are two files associated with wrapsfcn block, the S-function wrapper and the C code that contains the algorithm. This is the S-function wrapper code for this example, called wrapsfcn.c.
#define S_FUNCTION_NAME wrapsfcn #define S_FUNCTION_LEVEL 2 #include "simstruc.h"extern real_T my_alg(real_T u); /* * mdlInitializeSizes - initialize the sizes array */ static void mdlInitializeSizes(SimStruct *S) { ssSetNumSFcnParams( S, 0); /*number of input arguments*/ if (!ssSetNumInputPorts(S, 1)) return; ssSetInputPortWidth(S, 0, 1); ssSetInputPortDirectFeedThrough(S, 0, 1); if (!ssSetNumOutputPorts(S,1)) return; ssSetOutputPortWidth(S, 0, 1); ssSetNumSampleTimes( S, 1); } /* * mdlInitializeSampleTimes - indicate that this S-function runs *at the rate of the source (driving block) */ static void mdlInitializeSampleTimes(SimStruct *S) { ssSetSampleTime(S, 0, INHERITED_SAMPLE_TIME); ssSetOffsetTime(S, 0, 0.0); } /* * mdlOutputs - compute the outputs by calling my_alg, which *resides in another module, my_alg.c */ static void mdlOutputs(SimStruct *S, int_T tid) { InputRealPtrsType uPtrs = ssGetInputPortRealSignalPtrs(S,0); real_T *y = ssGetOutputPortRealSignal(S,0);
*y = my_alg(*uPtrs[0]); } /* * mdlTerminate - called when the simulation is terminated. */ static void mdlTerminate(SimStruct *S) { } #ifdef MATLAB_MEX_FILE /* Is this file being compiled as a MEX-file? */ #include "simulink.c" /* MEX-file interface mechanism */ #else #include "cg_sfun.h" /* Code generation registration function */ #endif
The S-function routine mdlOutputs contains a function call to my_alg, which is the C function that contains the algorithm that the S-function performs. This is the code for my_alg.c.
#include "tmwtypes.h"
real_T my_alg(real_T u)
{
return(u * 2.0);
}
The wrapper S-function (wrapsfcn) calls my_alg, which computes u * 2.0. To build wrapsfcn.mex, use the following command.
mex wrapsfcn.c my_alg.c
 | Writing Wrapper S-Functions | The TLC S-Function Wrapper |  |