| Symbolic Math Toolbox |   |
Generalized hypergeometric function
Syntax
Description
hypergeom(n, d, z) is the generalized hypergeometric function F(n, d, z), also known as the Barnes extended hypergeometric function and denoted by jFk where j = length(n) and k = length(d). For scalar a, b, and c, hypergeom([a,b],c,z) is the Gauss hypergeometric function 2F1(a,b;c;z).
The definition by a formal power series is
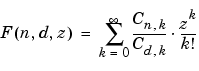
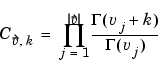
Either of the first two arguments may be a vector providing the coefficient parameters for a single function evaluation. If the third argument is a vector, the function is evaluated pointwise. The result is numeric if all the arguments are numeric and symbolic if any of the arguments is symbolic.
See Abramowitz and Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions, chapter 15.
Examples
hypergeom([],[],z) returns exp(z)
hypergeom(1,[],z) returns -1/(-1+z)
hypergeom(1,2,'z') returns (exp(z)-1)/z
hypergeom([1,2],[2,3],'z') returns 2*(exp(z)-1-z)/z^2
hypergeom(a,[],z) returns (1-z)^(-a)
hypergeom([],1,-z^2/4) returns besselj(0,z)
 | horner | ifourier |  |