| Real-Time Workshop |   |
Nonvirtual Subsystem Code Generation Options
For any nonvirtual subsystem, you can choose the following code generation options from the RTW system code pop-up menu in the subsystem Block parameters dialog:
Auto: This is the default option, and provides the greatest flexibility in most situations. See Auto Option below.
Inline: This option explicitly directs Real-Time Workshop to inline the subsystem unconditionally.
Function: This option explicitly directs Real-Time Workshop to generate a separate function with no arguments, and (optionally) place the subsystem in a separate file. You can name the generated function and file. As functions created with this option rely on global data, they are not re-entrant.
Reusable function: Generates a function with arguments, that allows the subsystem's code to be shared by other instances of it in the model. To enable sharing, Real-Time Workshop must be able to determine (via checksums) that subsystems are identical. The generated function will have arguments for block inputs and outputs, continuous states, parameters, etc.
The sections below further discuss the Auto, Inline, Function, and Reusable function options.
Auto Option
The Auto option is the default, and is generally appropriate. Auto causes Real-Time Workshop to inline the subsystem when there is only one instance of it in the model. When multiple instances of a subsystem exist, the Auto option will result in a single copy of the function whenever possible (as a reusable function). Otherwise, the result will be as though you selected Inline (except for function call subsystems with multiple callers, which will be handled as if you specified Function). Choose Inline to always inline subsystem code, or Function when you specifically want to generate a separate function without arguments for each instance, optionally in a separate file.
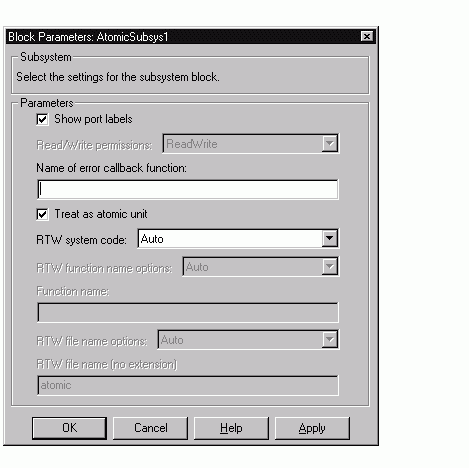
Figure 4-1: Auto Code Generation Option for a Nonvirtual Subsystem
Auto Optimization for Special Cases. Rather than reverting to Inline, the Auto option will optimize code in special situations in which identical subsystems contain other identical subsystems, by both reusing and inlining generated code. Suppose a model, such as schematized in Figure 4-2, contains identical subsystems A1 and A2. A1 contains subsystem B1, and A2 contains subsystem B2, which are themselves identical. In such cases, the Auto option will cause one function will be generated which will be called for both A1 and A2, and this function will contain one piece of inlined code to execute B1 and B2, insuring that the resulting code will run as efficiently as possible.
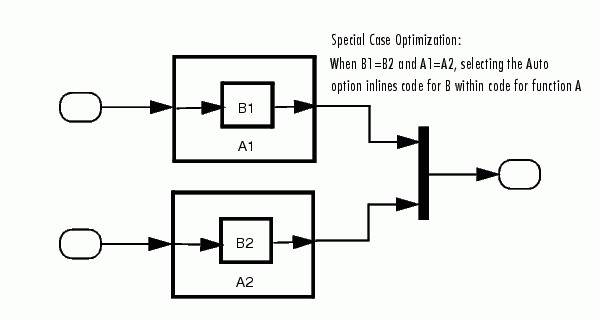
Figure 4-2: Reuse of Identical Nested Subsystems with the Auto Option
Inline Option
As noted above, you can choose to inline subsystem code when the subsystem is nonvirtual (virtual subsystems are always inlined).
Exceptions to Inlining. Note that there are certain cases in which Real-Time Workshop will not inline a nonvirtual subsystem, even though the Inline option is selected. These cases are:
SS_OPTION_FORCE_NONINLINED_FCNCALL to TRUE, it will not be inlined. This may be the case when user-defined Asynchronous Interrupt blocks or Task Synchronization blocks are required. Such blocks must be generated as functions. The VxWorks Asynchronous Interrupt and Task Synchronization blocks, shipped with Real-Time Workshop, use the SS_OPTION_FORCE_NONINLINED_FCNCALL option.
To generate inlined subsystem code:
Figure 4-3: Inlined Code Generation for a Nonvirtual Subsystem
When you generate code from your model, Real-Time Workshop writes inline code within model.c (or in its parent system's source file) to perform subsystem computations. You can identify this code by system/block identification tags, such as the following.
SeeTracing Generated Code Back to Your Simulink Model for further information on system/block identification tags.
Function Option
Choosing the function option (or Reusable function) lets you direct Real-Time Workshop to generate a separate function and (optionally) a separate file for the subsystem. When you select the Function option, two additional options are enabled:
Figure 4-4 shows the Block Parameters dialog with the Function option selected.
RTW Function Name Options Menu. This menu offers the following choices, but note that the resulting identifiers are also affected by which General code appearance options are in effect for the model:
Auto: By default, Real-Time Workshop assigns a unique function name using the default naming convention: model_subsystem(), where subsystem is the name of the subsystem (or that of an identical one when code is being reused). When the Include system hierarchy number in identifiers option of the General code appearance options is selected, a sequential identifier (s0, s1,...sn) assigned by Simulink and prefixed to the model name, e.g. sn_model_subsystem(). When the Prefix model name to global identifiers option of the General code appearance options is not selected, the above generic function identifier will take the form of sn_subsystem().
Use subsystem name: Real-Time Workshop uses the subsystem name as the function name. The General code appearance options Prefix model name to global identifiers option setting also affects the resulting identifiers.
User specified: When this option is selected, the RTW function name text entry field is enabled. Enter any legal function name. Note that the function name must be unique, and the General code appearance options settings are ignored for the function.
RTW File Name Options Menu. This menu offers the following choices:
Use subsystem name: Real-Time Workshop generates a separate file, using the subsystem (or library block) name as the filename.
Use function name: Real-Time Workshop generates a separate file, using the function name (as specified by the RTW function name options) as the filename.
User specified: When this option is selected, the RTW file name (no extension) text entry field is enabled. Real-Time Workshop generates a separate file, using the name you enter as the filename. Enter any filename desired, but do not include the .c (or any other) extension. This filename need not be unique.
Auto: Real-Time Workshop does not generate a separate file for the subsystem. Code generated from the subsystem is generated within the code module generated from the subsystem's parent system. If the subsystem's parent is the model itself, code generated from the subsystem is generated within model.c.
To generate both a separate subsystem function and a separate file:
Auto (options are described in RTW File Name Options Menu).
UserSpecified filename option.
Figure 4-4: Subsystem Function Code Generation
with Separate User-Defined File Name
Reusable Function Option
The difference between functions and reusable functions is that the latter have data passed to them as arguments (enabling them to be re-entrant), while the former communicate via global data. Choosing the Reusable function option directs Real-Time Workshop to generate a single function (optionally in a separate file) for the subsystem, and to call that code for each identical subsystem in the model, if possible.
Subsystems that are superfically identical still may not generate reusable code. Specifically, Real-Time Workshop is not able to reuse subsystems having any of the following characteristics:
Some of these situations can arise even when subsystems are copied and pasted within or between models or are manually constructed to be identical. If Real-Time workshop determines that code for a subsystem cannot be reused, it will output the subsystem as a function with arguments when Reusable function is selected, but the function will not be reused. If you prefer that subsystem code be inlined in such circumstances rather than deployed as functions, you should choose Auto for the RTW system code option.
The presence of certain blocks in a subsystem can also prevent its code from being reused. These are:
Regarding S-function blocks, there are several requirements that need to be met in order for subsystems containing them to be reused. See Creating Code-Reuse-Compatible S-Functions in the Simulink documentation.
When you select the Reusable function option, two additional options are enabled. See the explanation of Function Option for descriptions of these options and fields. If you enter names in these fields, you must specify exactly the same function name and filename for each instance of identical subsystems for Real-Time Workshop to be able to reuse the subsytem code.
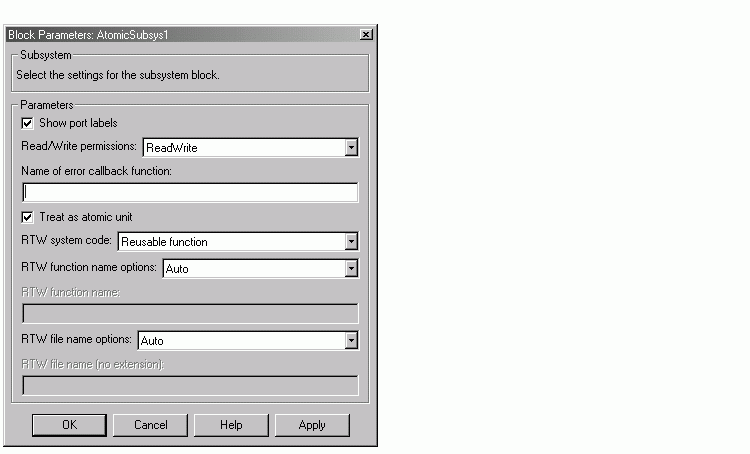
Figure 4-5: Subsystem Reusable Function Code Generation Option
To request that Real-Time Workshop generate reusable subsystem code:
Resusable function from the RTW system code menu as shown in Figure 4-5.
Auto option, and want code to be reused, you must assign exactly the same function name to all other subsystem blocks that you want to share this code.
Auto (options are described in RTW File Name Options Menu).
 | Nonvirtual Subsystem Code Generation | Modularity of Subsystem Code |  |