| SimPowerSystems |   |
Setting the Initial Load Flow and Obtaining Steady State
Before performing transient tests you must initialize your model for the desired load flow. Use the load flow utility of the powergui to obtain an active power flow of 1500 MW out of the machine with a terminal voltage of 1 p.u. (13.8 kV).
Open the powergui and select Load Flow and Machine Initialization. A new window appears. In the upper right window you have the name of the only machine present in your system. Its Bus Type should be PV Generator and the desired Terminal Voltage should already be set to the nominal voltage of 13800 V. In the Active Power field, enter 1500e6 as the desired output power. Click the Execute load flow button. Once the load flow is solved, the phasors of AB and BC machine voltages as well as currents flowing in phases A and B are updated in the left window. The required mechanical power to drive the machine is displayed in watts and in p.u., and the required excitation voltage E is displayed in p.u.
Notice that constant blocks containing these two values are already connected to the Pm and E inputs of the machine block. If you open the machine dialog box, you see that the machine initial conditions (initial speed deviation dw = 0; internal angle theta, current magnitudes, and phase angles) are automatically transferred in the last line.
Once the load flow is performed, you can obtain the corresponding voltage and current measurements at the different buses. In the powergui select Steady State Voltages and Currents. You can observe, for example, the phasors for phase A voltages at buses B1, B2, and B3 and the current entering line 1 at bus B1.
B1/Va : 6.088e5 V ; 18.22 degreesB2/Va : 6.223e5 V ; 9.26 degreesB3/Va : 6.064e5 V ; 2.04 degreesB1/Ia : 1560 A ; 30.50 degrees
The active power flow for phase A entering line 1 is therefore
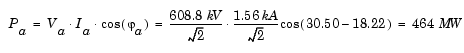
corresponding to a total of 464 * 3 = 1392 MW for the three phases.
 | Series-Compensated Transmission Network | Transient Performance for a Line Fault |  |