| GARCH Toolbox |   |
Contents of the Specification Structure
This example shows the contents of the specification structure. It is the specification structure, coeff, for the default model. The term to the left of the colon (:) is the parameter name.
coeff coeff = Comment: 'Mean: ARMAX(0,0,0); Variance: GARCH(1,1)' R: 0 M: 0 P: 1 Q: 1 Distribution: 'Gaussian' C: 4.9183e-004 AR: [] MA: [] Regress: [] K: 8.2736e-007 GARCH: 0.9628 ARCH: 0.0318 FixC: [] FixAR: [] FixMA: [] FixRegress: [] FixK: [] FixGARCH: [] FixARCH: [] Optimization: [1x1 struct]
The specification structure parameters of interest in this discussion are Comment, R, M, P, Q, C, AR, MA, Regress, K, GARCH, and ARCH. (See the garchset reference page for a complete description of the GARCH specification structure parameters.) This section discusses:
The Comment Field
The Comment field summarizes the ARMAX and GARCH models used for the conditional mean and variance equations in the default model example. The Comment value 'Mean: ARMAX(0,0,0); Variance: GARCH(1,1)' describes the default model in terms of the general ARMAX(R,M,Nx) form for the conditional mean, where R = M = Nx = 0
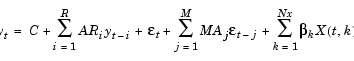
|
(2-14) |
and the general GARCH(P,Q) form with Gaussian innovations for the conditional variance, where P = Q = 1.
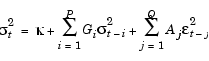
|
(2-15) |
By default, garchfit and garchset generate the Comment field automatically Although you can set the value of the Comment field, it offers such a convenient summary that The MathWorks discourages your doing so. However, if you do specify your own comment, the GARCH Toolbox recognizes this and does not override your comment.
Equation Variables and Parameter Names
For the most part, the names of specification structure parameters that define the ARMAX/GARCH models reflect the variable names of their corresponding components in Eq. (2-14) and Eq. (2-15):
R and M represent the order of the ARMA(R,M) model.
P and Q represent the order of the GARCH(P,Q) model.
AR represents the coefficient vector ARi.
MA represents the coefficient vector MAj.
GARCH represents the coefficient vector Gi.
ARCH represents the coefficient vector Aj.
C and K represent the constants C and 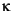 , respectively.
, respectively.
Unlike the other components of these equations, X has no representation in the GARCH specification structure. X is an optional matrix of returns that some toolbox functions use as explanatory variables in the regression component of the conditional mean. For example, X could contain return series of a suitable market index collected over the same period as y. Toolbox functions that allow the use of a regression matrix provide a separate argument by which you can specify it. In the specification structure, Regress represents the coefficient vector of X, 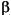 k.
k.
Interpreting the Specification Structure
In the specification structure, coeff, for the default model example, the AR, MA, and Regress fields are empty matrices ([]). This is because the default mean equation is an ARMAX(0,0,0) model, where R = M = Nx = 0, and AR, MA, and Regress are R-, M-, and Nx-element vectors, respectively.
The GARCH and ARCH fields are both scalars set to their respective estimated values. They are scalars because the default variance equation is a GARCH(1,1) model, where P = 1 lag of the past conditional variance and Q = 1 lag of the past squared innovations.
C and K are the constants of the mean and variance equations, respectively. Their values were estimated by garchfit.
 | Purpose of the Specification Structure | Valid Model Specifications |  |