| Communications Blockset |
  |
Rectangular QAM Modulator Baseband
Modulate using M-ary quadrature amplitude modulation
Library
AM, in Digital Baseband sublibrary of Modulation
Description

The Rectangular QAM Modulator Baseband block modulates using M-ary quadrature amplitude modulation with a constellation on a rectangular lattice. The output is a baseband representation of the modulated signal.
Constellation Size and Scaling
The signal constellation has M points, where M is the M-ary number parameter. M must have the form 2K for some positive integer K. The block scales the signal constellation based on how you set the Normalization method parameter. The table below lists the possible scaling conditions
Value of Normalization method parameter
|
Scaling Condition
|
Min. distance between symbols
|
The nearest pair of points in the constellation is separated by the value of the Minimum distance parameter.
|
Average Power
|
The average power of the symbols in the constellation is the Average power parameter.
|
Peak Power
|
The maximum power of the symbols in the constellation is the Peak power parameter.
|
.
Input Signal Values
The input and output for this block are discrete-time signals. The Input type parameter determines whether the block accepts integers between 0 and M-1, or binary representations of integers:
- If Input type is set to Integer, then the block accepts integers. The input can be either a scalar or a frame-based column vector.
- If Input type is set to Bit, then the block accepts groups of K bits, called binary words. The input can be either a vector of length K or a frame-based column vector whose length is an integer multiple of K. The Constellation ordering parameter indicates how the block assigns binary words to points of the signal constellation. Such assignments apply independently to the in-phase and quadrature components of the input:
- If Constellation ordering is set to Binary, then the block uses a natural binary-coded constellation.
- If Constellation ordering is set to Gray and K is even, then the block uses a Gray-coded constellation.
- If Constellation ordering is set to Gray and K is odd, then the block codes the constellation so that pairs of nearest points differ in one or two bits. The constellation is cross-shaped, and the schematic below indicates which pairs of points differ in two bits. The schematic uses M = 128, but suggests the general case.

For details about the Gray coding, see the reference page for the M-PSK Modulator Baseband block and the paper listed in References below. Note that since the in-phase and quadrature components are assigned independently, the Gray and binary orderings coincide when M = 4.
Upsampling the Modulated Signal
This block can output an upsampled version of the modulated signal. The Samples per symbol parameter is the upsampling factor. It must be a positive integer. For more information, see Upsampled Signals and Rate Changes in Using the Communications Blockset.
Dialog Box
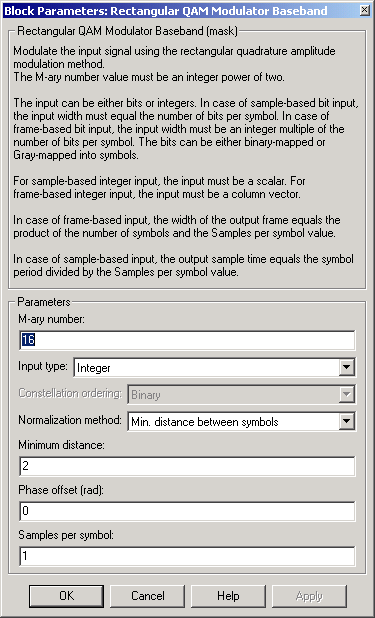
- M-ary number
- The number of points in the signal constellation. It must have the form 2K for some positive integer K.
- Input type
- Indicates whether the input consists of integers or groups of bits.
- Constellation ordering
- Determines how the block maps each group of input bits to a corresponding integer. This field is active only when Input type is set to Bit.
- Normalization method
- Determines how the block scales the signal constellation. Choices are Min. distance between symbols, Average Power, and Peak Power.
- Minimum distance
- The distance between two nearest constellation points. This field appears only when Normalization method is set to Min. distance between symbols.
- Average power (watts)
- The average power of the symbols in the constellation. This field appears only when Normalization method is set to Average Power.
- Peak power (watts)
- The maximum power of the symbols in the constellation. This field appears only when Normalization method is set to Peak Power.
- Phase offset (rad)
- The rotation of the signal constellation, in radians.
- Samples per symbol
- The number of output samples that the block produces for each integer or binary word in the input.
Pair Block
Rectangular QAM Demodulator Baseband
See Also
General QAM Modulator Baseband
References
[1] Smith, Joel G. "Odd-Bit Quadrature Amplitude-Shift Keying." IEEE
Transactions on Communications, vol. COM-23, March 1975. 385-389.
 | Rectangular QAM Demodulator Passband | | Rectangular QAM Modulator Passband |  |






