

| MATLAB Function Reference |   |
Evaluate the numerical solution of a PDE using the output of pdepe
Syntax
Arguments
|
Symmetry of the problem: slab = 0, cylindrical = 1, spherical = 2. This is the first input argument used in the call to pdepe. |
xmesh |
A vector [x0, x1, ..., xn] specifying the points at which the elements of ui were computed. This is the same vector with which pdepe was called. |
ui |
A vector |
|
A vector of points from the interval [ |
Description
[uout,duoutdx] = pdeval(m,x,ui,xout)
approximates the solution 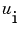 and its partial derivative
and its partial derivative 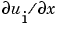 at points from the interval [
at points from the interval [x0,xn]. The pdeval function returns the computed values in uout and duoutdx, respectively.
Note
pdeval evaluates the partial derivative 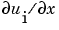 rather than the flux rather than the flux 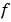 . Although the flux is continuous, the partial derivative may have a jump at a material interface. . Although the flux is continuous, the partial derivative may have a jump at a material interface.
|
See Also
 | pdepe | peaks |  |