
| xPC Target |   |
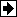
Scaling Input to Output
| Hardware Input |
Block Output Data Type |
Scaling |
| volts |
double |
1 |
Driver Block Parameters
Carrier ID -- Enter the Carrier ID of the IP carrier board into which the IP module is plugged.
In order to use an IP module, it must be physically plugged into an IP carrier board and the model must contain a block representing this carrier board. Each carrier block has a `Carrier ID' parameter, which must be set to a number not shared by any other carrier board block in the model.
Carrier slot -- Select the slot on the carrier board into which the IP-16ADC module is plugged. Note that different carrier boards can have different slot capacities.
Channel vector -- Enter a vector of numbers between 1 and 16. The channel numbers can occur in any order. For example, to use the first and third analog output (A/D) channels, enter
Number the channels beginning with 1 even if the board manufacturer starts numbering the channels with 0.
Range vector -- Enter a range code for each of the channels in the channel vector. The range vector must be the same length as the channel vector. This board allows the range of each channel to be different.
The following table is a list of the ranges for this driver and the corresponding range codes.
| Range Code |
Input Range (V) |
| -10 |
-10 to +10 |
| -5 |
-5 to +5 |
| 5 |
0 to 5 |
| 10 |
0 to 10 |
Range codes -10 and -5 specify differential channels, which each use two pins on the I/O cable. Range codes 10 and 5 specify single-ended channels, which each use only one pin. Certain combinations of channel numbers and range codes can refer to conflicting physical I/O pins and will cause an error of the form "Bipolar channel x and unipolar channel y use the same I/O pins". Consult the section "I/O Pin Wiring" in the IP-16ADC User's Manual as you select the channel and range vectors to avoid this.
Sample time -- Enter the base sample time or a multiple of the base sample time.
 | IP-16ADC | IP-16DAC |  |