| Database Toolbox |   |
Exporting Data from MATLAB to a New Record in a Database
In this example, you retrieve a set of data, perform a simple calculation on the data using MATLAB, and export the results as a new record to another table in the database. Specifically, you retrieve freight costs from an orders table, calculate the average freight cost, put the data into a cell array to export it. Then export the data (the average freight cost and the date the calculation was made) to an empty table.
You learn to use these Database Toolbox functions:
northwind database to be sure it is writable,
that is, not read only.
northwind database in Microsoft Access.
Calc_Date and Avg_Cost.
Calc_Date field, use the default Data Type, which is Text, and
for the Avg_Cost field, set the Data Type to Number.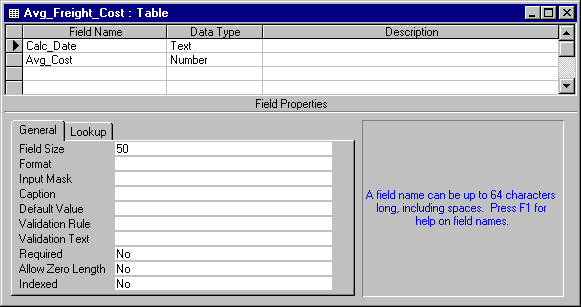
Avg_Freight_Cost and close it. Access warns you that
there is no primary key, but you do not need one. If you do designate a
primary key, you can only run the example once because Access prevents
you from inserting the same record twice.
After creating the table in Access, if you want to run a set of functions similar to this example, use the M-file matlab\toolbox\database\dbdemos\dbinsertdemo.m.
SampleDB. Type
numeric by typing
numeric, which is needed to perform calculations on the data.
freight column of data from the orders table. To keep the example simple, import only three rows of data. Type
numrows. Then calculate the average, assigning the result to the variable meanA. Type
D by typing
setdbprefs, but instead use standard MATLAB operations to define it. Put the date in the first cell by typing
Avg_Freight_Cost table you created earlier, Calc_Date and Avg_Cost. Assign the cell array containing the column names to the variable colnames. Type
AutoCommit flag for the database. The status of the AutoCommit flag determines if the database data will be automatically committed or not. If the flag is off, you can undo an update.
AutoCommit flag using the get function by typing
The AutoCommit flag is set to on so exported data will be automatically committed. In this example, keep the AutoCommit flag on; for a Microsoft Access database, this is the only option.
conn is the connection object for the database to which you are exporting data. In this example, conn is SampleDB, which is already open. However, if you export to a different database that is not open, use the database function to connect to it before exporting the data.
Avg_Freight_Cost is the name of the table to which you are exporting data. In the insert function, you also include the colnames cell array and the cell array containing the data you are exporting, exdata, both of which you defined in the previous steps. Note that you do not define the type of data you are exporting; the data is exported in its current MATLAB format.
Running insert appends the data as a new record at the end of the Avg_Freight_Cost table.
If you get an error, it may be because the table is open in design mode in Access. Close the table in Access and repeat the insert function.
Avg_Cost value was rounded to a whole number to match the properties of that field in Access.
Avg_Freight_Cost table in Access because you will use it in the next example.
 | Viewing Information About the Imported Data | Replacing Existing Data in a Database MATLAB |  |