| Data Acquisition Toolbox |   |
The Data Acquisition Engine
The data acquisition engine (or just engine) is a MEX-file dynamic link library (DLL) file that
While the engine performs these tasks, you can use MATLAB for other tasks such as analyzing acquired data. In other words, the engine and MATLAB are asynchronous. The relationship between acquiring data, outputting data, and data flow is described below.
The Flow of Acquired Data
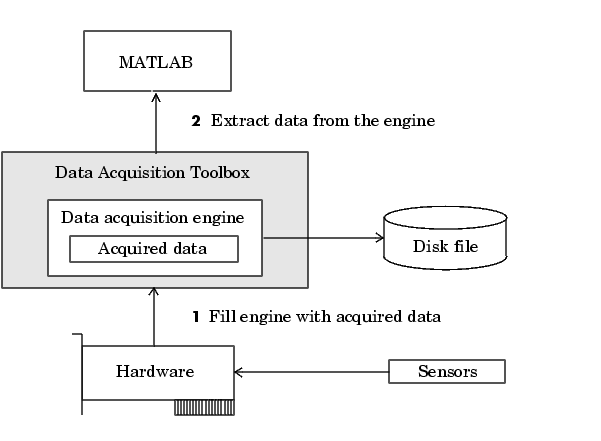
Acquiring data means that data is flowing from your hardware device into the data acquisition engine where it is temporarily stored in memory. The data is stored temporarily because it can be overwritten. The rate at which the data is overwritten depends on several factors including the available memory, the rate at which data is acquired, and the number of hardware channels from which data is acquired.
The stored data is not automatically available in the MATLAB workspace. Instead, you must explicitly extract data from the engine using the getdata function.
The flow of acquired data consists of these two independent steps:
These two steps are illustrated below.
The Flow of Output Data
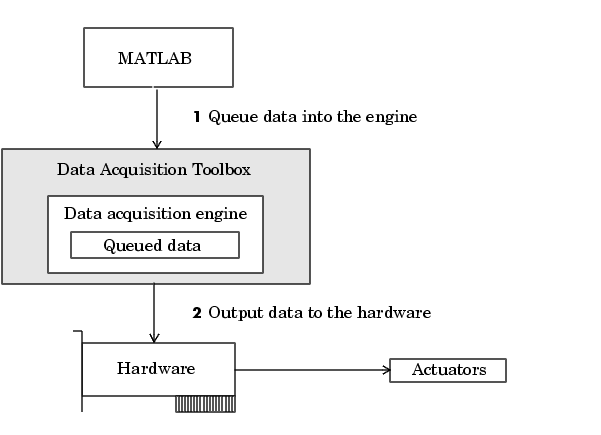
Outputting data means that data is flowing from the data acquisition engine to the hardware device. However, before data is output, you must queue it in the engine with the putdata function. The amount of data that you can queue depends on several factors including the available memory, the number of hardware channels to which data is output, and the size of each data sample.
The flow of output data consists of these two independent steps:
These two steps are illustrated below.
 | M-File Functions | The Hardware Driver Adaptor |  |