| Data Acquisition Toolbox |   |
Data Acquisition Hardware
Data acquisition hardware is either internal and installed directly into an expansion slot inside your computer, or external and connected to your computer through an external cable. For example, VXI modules are installed in an external VXI chassis, and data is transferred between MATLAB and the module using an external link such as FireWire (IEEE 1394).
At the simplest level, data acquisition hardware is characterized by the subsystems it possesses. A subsystem is a component of your data acquisition hardware that performs a specialized task. Common subsystems include
Hardware devices that consist of multiple subsystems, such as the one depicted below, are called multifunction boards.
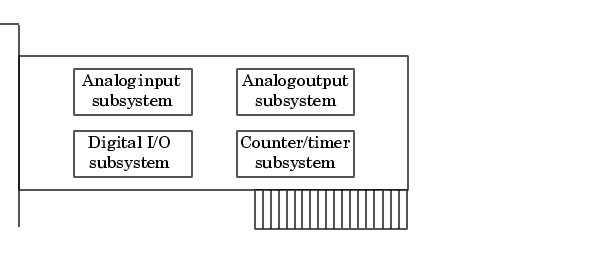
Analog Input Subsystems
Analog input subsystems convert real-world analog input signals from a sensor into bits that can be read by your computer. Perhaps the most important of all the subsystems commonly available, they are typically multichannel devices offering 12 or 16 bits of resolution.
Analog input subsystems are also referred to as AI subsystems, A/D converters, or ADCs. Analog input subsystems are discussed in detail beginning in The Analog Input Subsystem.
Analog Output Subsystems
Analog output subsystems convert digital data stored on your computer to a real-world analog signal. These subsystems perform the inverse conversion of analog input subsystems. Typical acquisition boards offer two output channels with 12 bits of resolution, with special hardware available to support multiple channel analog output operations.
Analog output subsystems are also referred to as AO subsystems, D/A converters, or DACs.
Digital Input/Output Subsystems
Digital input/output (DIO) subsystems are designed to input and output digital values (logic levels) to and from hardware. These values are typically handled either as single bits or lines, or as a port, which typically consists of eight lines.
While most popular data acquisition cards include some digital I/O capability, it is usually limited to simple operations, and special dedicated hardware is often necessary for performing advanced digital I/O operations.
Counter/Timer Subsystems
Counter/timer (C/T) subsystems are used for event counting, frequency and period measurement, and pulse train generation.
 | The Data Acquisition System | Sensors |  |