| Function Reference |   |
Compute controllability and observability grammians
Syntax
Description
gram
calculates controllability and observability grammians. You can use grammians to study the controllability and observability properties of state-space models and for model reduction [1,2]. They have better numerical properties than the controllability and observability matrices formed by ctrb and obsv.
Given the continuous-time state-space model
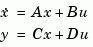
the controllability grammian is defined by
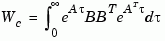
and the observability grammian by

The discrete-time counterparts are
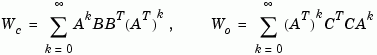
The controllability grammian is positive definite if and only if 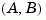 is controllable. Similarly, the observability grammian is positive definite if and only if
is controllable. Similarly, the observability grammian is positive definite if and only if 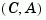 is observable.
is observable.
to compute the grammians of a continuous or discrete system. The LTI model sys must be in state-space form.
Algorithm
The controllability grammian 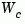 is obtained by solving the continuous-time Lyapunov equation
is obtained by solving the continuous-time Lyapunov equation
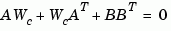
or its discrete-time counterpart
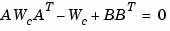
Similarly, the observability grammian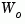 solves the Lyapunov equation
solves the Lyapunov equation
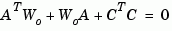
in continuous time, and the Lyapunov equation
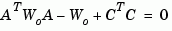
Limitations
The 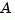 matrix must be stable (all eigenvalues have negative real part in continuous time, and magnitude strictly less than one in discrete time).
matrix must be stable (all eigenvalues have negative real part in continuous time, and magnitude strictly less than one in discrete time).
See Also
balreal
ctrb
lyap, dlyap
obsv
References
[1] Kailath, T., Linear Systems, Prentice-Hall, 1980.
 | get | hasdelay |  |