| Function Reference |   |
Specify descriptor state-space models
Syntax
sys = dss(a,b,c,d,e) sys = dss(a,b,c,d,e,Ts) sys = dss(a,b,c,d,e,ltisys) sys = dss(a,b,c,d,e,'Property1',Value1,...,'PropertyN',ValueN) sys = dss(a,b,c,d,e,Ts,'Property1',Value1,...,'PropertyN',ValueN)
Description
sys = dss(a,b,c,d,e)
creates the continuous-time descriptor state-space model
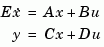
The 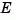 matrix must be nonsingular. The output
matrix must be nonsingular. The output sys is an SS model storing the model data (see "LTI Objects" on page 2-3). Note that ss produces the same type of object. If the matrix 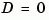 , do can simply set
, do can simply set d to the scalar 0 (zero).
sys = dss(a,b,c,d,e,Ts)
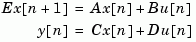
with sample time Ts (in seconds).
sys = dss(a,b,c,d,e,ltisys)
ltisys (including the sample time). See "LTI Properties" on page 2-26 for an overview of generic LTI properties.
Any of the previous syntaxes can be followed by property name/property value pairs
Each pair specifies a particular LTI property of the model, for example, the input names or some notes on the model history. See set and the example below for details.
Example
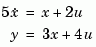
with a 0.1 second input delay. The input is labeled 'voltage', and a note is attached to tell you that this is just an example.
See Also
dssdata Retrieve 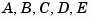 matrices of descriptor model
matrices of descriptor model
get Get properties of LTI models
set Set properties of LTI models
ss Specify (regular) state-space models
 | dsort | dssdata |  |