

| Communications Blockset |   |
Generate Rician distributed noise
Library
Noise Generators sublibrary of Comm Sources
Description 
The Rician Noise Generator block generates Rician distributed noise. The Rician probability density function is given by
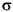 is the standard deviation of the Gaussian distribution that underlies the Rician distribution noise
is the standard deviation of the Gaussian distribution that underlies the Rician distribution noise
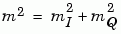 , where mI and mQ are the mean values of two independent Gaussian components
, where mI and mQ are the mean values of two independent Gaussian components
Note that m and 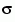 are not the mean value and standard deviation for the Rician noise.
are not the mean value and standard deviation for the Rician noise.
You must specify the Initial seed for the random number generator. When it is a constant, the resulting noise is repeatable. The vector length of the Initial seed parameter should equal the number of columns in a frame-based output or the number of elements in a sample-based output. The set of numerical parameters above the Initial seed parameter in the dialog box can consist of vectors having the same length as the Initial seed, or scalars.
Initial Seed
The scalar Initial seed parameter initializes the random number generator that the block uses to generate its Rician-distributed complex random process. For best results, the Initial seed should be a prime number greater than 30. Also, if there are other blocks in a model that have an Initial seed parameter, you should choose different initial seeds for all such blocks.
You can choose seeds for the Rician Noise Generator block using the Communications Blockset's randseed function. At the MATLAB prompt, type the command
This returns a random prime number greater than 30. Typing randseed again produces a different prime number. If you add an integer argument, randseed always returns the same prime for that integer. For example, randseed(5) always returns the same answer.
Attributes of Output Signal
The output signal can be a frame-based matrix, a sample-based row or column vector, or a sample-based one-dimensional array. These attributes are controlled by the Frame-based outputs, Samples per frame, and Interpret vector parameters as 1-D parameters. See Signal Attribute Parameters for Random Sources in Using the Communications Blockset for more details.
The number of elements in the Initial seed and Sigma parameters becomes the number of columns in a frame-based output or the number of elements in a sample-based vector output. Also, the shape (row or column) of the Initial seed and Sigma parameters becomes the shape of a sample-based two-dimensional output signal.
Dialog Box
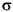 2), where m is as in the Rician probability density function. This field appears only if Specification method is K-factor.
2), where m is as in the Rician probability density function. This field appears only if Specification method is K-factor.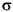 in the Rician probability density function.
in the Rician probability density function.See Also
References
[1] Proakis, John G. Digital Communications, Third edition. New York: McGraw Hill, 1995.
 | Rician Fading Channel | Sampled Quantizer Encode |  |