| Communications Blockset |
  |
Receiver Thermal Noise
Apply receiver thermal noise to a complex baseband signal
Library
RF Impairments
Description

The Receiver Thermal Noise block simulates the effects of thermal noise on a complex, baseband signal. You can specify the amount of thermal noise in three ways, according to which Specification method you select:
- Noise temperature - specifies the noise in degrees Kelvin
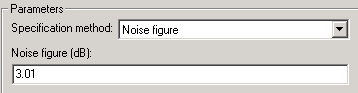
- Noise figure - specifies the noise in decibels relative to a noise temperature of 290 degrees Kelvin
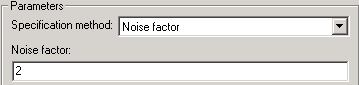
- Noise factor - specifies the noise in by the following equation6:
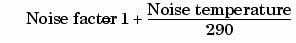
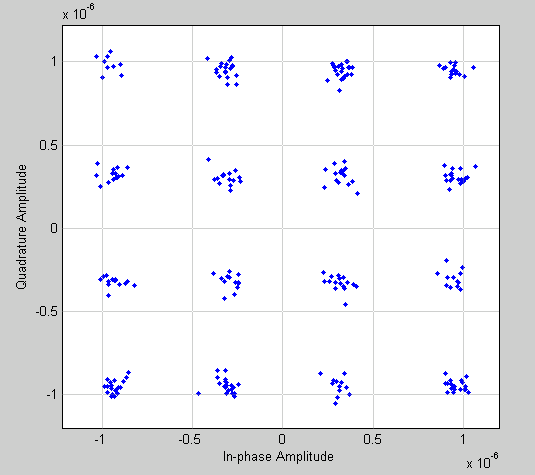
The following scatter plot shows the effect of the Receiver Thermal Noise block, with Specification method set to Noise Figure and Noise figure (db) set to 3.01, on a signal modulated by 16 -QAM.
 S
S
This plot is generated by the model described in Scatter Plot Examples, with the following parameter settings:
- Rectangular QAM Modulator Baseband
- Normalization method set to Average Power
- Average power (watts) set to
1e-12
- Receiver Thermal Noise
- Specification method set to Noise figure
- Noise figure (dB) set to
3.01
Dialog Box
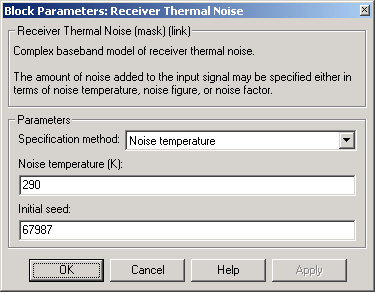
- Specification method
- The method by which you specify the amount of noise. The choices are Noise temperature, Noise figure, and Noise factor.
- Noise temperature (K)
- Scalar specifying the amount of noise in degrees Kelvin.
- Noise figure
- Scalar specifying the amount of noise in decibels relative to a noise temperature of 290 degrees Kelvin. A Noise figure setting of 0 dB indicates a noiseless system.
- Noise factor
- Scalar specifying the amount of noise relative to a noise temperature of 290 degrees Kelvin.
- Initial seed
- The initial seed value for the random number generator that generates the noise.
See Also
Free Space Path Loss
 | Rayleigh Noise Generator | | Rectangular QAM Demodulator Baseband |  |







