

| Communications Blockset |   |
Modulate using the quaternary phase shift keying method
Library
PM, in Digital Baseband sublibrary of Modulation
Description 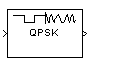
The QPSK Modulator Baseband block modulates using the quaternary phase shift keying method. The output is a baseband representation of the modulated signal.
Inputs and Constellation Types
If the Input type parameter is set to Integer, then valid input values are 0, 1, 2, and 3. If the input is m, then the output symbol is
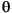 + j
+ j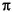 m/2)
m/2)
where 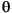 is the Phase offset parameter. In this case, the input can be either a scalar or a frame-based column vector.
is the Phase offset parameter. In this case, the input can be either a scalar or a frame-based column vector.
If the Input type parameter is set to Bit, then the input contains pairs of binary values. The input can be either a vector of length two or a frame-based column vector whose length is an even integer. If the Phase offset parameter is set to pi/4, then the block uses one of the signal constellations in the figure below, depending on whether the Constellation ordering parameter is set to Binary or Gray.
Upsampling the Modulated Signal
This block can output an upsampled version of the modulated signal. The Samples per symbol parameter is the upsampling factor. It must be a positive integer. For more information, see Upsampled Signals and Rate Changes in Using the Communications Blockset.
Dialog Box
Pair Block
See Also
M-PSK Modulator Baseband, BPSK Modulator Baseband, DQPSK Modulator Baseband
 | QPSK Demodulator Baseband | Quantizer Decode |  |