

| Communications Toolbox |   |
Compute number of symbol errors and symbol error rate
Syntax
For All Syntaxes
The symerr function compares binary representations of elements in x with those in y. The schematics below illustrate how the shapes of x and y determine which elements symerr compares.
The output number is a scalar or vector that indicates the number of elements that differ. The size of number is determined by the optional input flg and by the dimensions of x and y. The output ratio equals number divided by the total number of elements in the smaller input.
For Specific Syntaxes
[number,ratio] = symerr(x,y)
compares the elements in x and y. The sizes of x and y determine which elements are compared:
x and y are matrices of the same dimensions, then symerr compares x and y element-by-element. number is a scalar. See schematic (a) in the figure.
symerr compares the vector element-by-element with each row (resp., column) of the matrix. The length of the vector must equal the number of columns (resp., rows) in the matrix. number is a column (resp., row) vector whose mth entry indicates the number of elements that differ when comparing the vector with the mth row (resp., column) of the matrix. See schematics (b) and (c) in the figure.
[number,ratio] = symerr(x,y, is similar to the previous syntax, except that flg)
flg can override the defaults that govern which elements symerr compares and how symerr computes the outputs. The values of flg are 'overall', 'column-wise', and 'row-wise'. The table below describes the differences that result from various combinations of inputs. In all cases, ratio is number divided by the total number of elements in y.
[number,ratio,loc] = symerr(...)
returns a binary matrix loc that indicates which elements of x and y differ. An element of loc is zero if the corresponding comparison yields no discrepancy, and one otherwise.
Examples
On the reference page for biterr, the last example uses symerr.
The command below illustrates how symerr works when one argument is a vector and the other is a matrix. It compares the vector [1,2,3]' to the columns
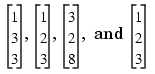
As another example, the command below illustrates the use of flg to override the default row-by-row comparison. Notice that number and ratio are scalars.
format rat; [number,ratio,loc] = symerr([1 2; 3 4],...
[1 3],'overall')
number =
3
ratio =
3/4
loc =
0 1
1 1
See Also
biterr
 | shift2mask | syndtable |  |