

| MATLAB Function Reference |   |
Syntax
Description
C = conv2(A,B)
computes the two-dimensional convolution of matrices A and B. If one of these matrices describes a two-dimensional finite impulse response (FIR) filter, the other matrix is filtered in two dimensions.
The size of C in each dimension is equal to the sum of the corresponding dimensions of the input matrices, minus one. That is, if the size of A is [ma,na] and the size of B is [mb,nb], then the size of C is [ma+mb-1,na+nb-1].
C = conv2(hcol,hrow,A)
convolves A first with the vector hcol along the rows and then with the vector hrow along the columns. If hcol is a column vector and hrow is a row vector, this case is the same as C = conv2(hcol*hrow,A).
C = conv2(...,'shape')
returns a subsection of the two-dimensional convolution, as specified by the shape parameter:
Algorithm
conv2 uses a straightforward formal implementation of the two-dimensional convolution equation in spatial form. If 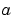 and
and 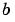 are functions of two discrete variables,
are functions of two discrete variables, 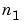 and
and 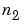 , then the formula for the two-dimensional convolution of
, then the formula for the two-dimensional convolution of 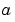 and
and 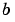 is
is
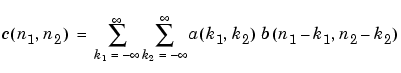
In practice however, conv2 computes the convolution for finite intervals.
Note that matrix indices in MATLAB always start at 1 rather than 0. Therefore, matrix elements A(1,1), B(1,1), and C(1,1) correspond to mathematical quantities a(0,0), b(0,0), and c(0,0).
Examples
Example 1. For the 'same' case, conv2 returns the central part of the convolution. If there are an odd number of rows or columns, the "center" leaves one more at the beginning than the end.
This example first computes the convolution of A using the default ('full') shape, then computes the convolution using the 'same' shape. Note that the array returned using 'same' corresponds to the underlined elements of the array returned using the default shape.
A = rand(3); B = rand(4); C = conv2(A,B) % C is 6-by-6 C = 0.1838 0.2374 0.9727 1.2644 0.7890 0.3750 0.6929 1.2019 1.5499 2.1733 1.3325 0.3096 0.5627 1.5150 2.3576 3.1553 2.5373 1.0602 0.9986 2.3811 3.4302 3.5128 2.4489 0.8462 0.3089 1.1419 1.8229 2.1561 1.6364 0.6841 0.3287 0.9347 1.6464 1.7928 1.2422 0.5423 Cs = conv2(A,B,'same') % Cs is the same size as A: 3-by-3 Cs = 2.3576 3.1553 2.5373 3.4302 3.5128 2.4489 1.8229 2.1561 1.6364
Example 2. In image processing, the Sobel edge finding operation is a two-dimensional convolution of an input array with the special matrix
These commands extract the horizontal edges from a raised pedestal.
Transposing the filter s extracts the vertical edges of A.
This figure combines both horizontal and vertical edges.
See Also
xcorr2 in the Signal Processing Toolbox
 | conv | convhull |  |