

| MATLAB Function Reference |   |
Syntax
Description
P = atan2(Y,X)
returns an array P the same size as X and Y containing the element-by-element, four-quadrant inverse tangent (arctangent) of the real parts of Y and X. Any imaginary parts are ignored.
Elements of P lie in the closed interval [-pi,pi], where pi is the MATLAB floating-point representation of 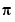 .
. atan uses sign(Y) and sign(X) to determine the specific quadrant.
atan2(Y,X) contrasts with atan(Y/X), whose results are limited to the interval 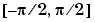 , or the right side of this diagram.
, or the right side of this diagram.
Examples
Any complex number 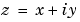 is converted to polar coordinates with
is converted to polar coordinates with
This is a common operation, so MATLAB provides a function, angle(z), that computes theta = atan2(imag(z),real(z)).
To convert back to the original complex number
Algorithm
atan2 uses FDLIBM, which was developed at SunSoft, a Sun Microsystems, Inc. business, by Kwok C. Ng, and others. For information about FDLIBM, see http://www.netlib.org.
See Also
 | atan | atanh |  |